Inhibition of IkappaB kinase-beta protects dopamine neurons against lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity
- PMID: 20190013
- PMCID: PMC2879929
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.110.165829
Inhibition of IkappaB kinase-beta protects dopamine neurons against lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity
Abstract
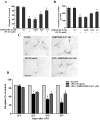
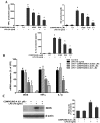
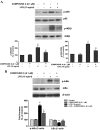
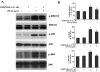
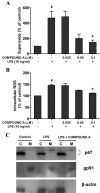
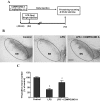
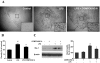
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurological disorder characterized by a selective loss of dopamine (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra (SN). Although current therapy can control symptoms of this disorder, there is no effective therapy available to halt its progression. Recently, neuroinflammation has been recognized as an important contributor to the pathogenesis of PD, and nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) plays a key role in regulating neuroinflammation. Hence, the modulation of NF-kappaB pathway may have therapeutic potential for PD. Activation of NF-kappaB depends on the phosphorylation of its inhibitor, IkappaB, by the specific IkappaB kinase (IKK) subunit IKK-beta. Compound A (7-[2-(cyclopropylmethoxy)-6-hydroxyphenyl]-5-[(3S)-3-piperidinyl]-1, 4-dihydro-2H-pyrido[2,3-d][1,3]oxazin-2-one hydrochloride), a potent and selective inhibitor of IKK-beta, has recently been reported to provide cardioprotection through specific suppression of NF-kappaB signaling. The present study, for the first time, elucidates neuroprotective effects of compound A. Daily subcutaneous injection of compound A (1 mg/kg) for 7 days inhibited the activation of microglia induced by nigral stereotaxic injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and significantly attenuated LPS-induced loss of DA neurons in the SN. In vitro mechanistic studies revealed that neuroprotective effects of compound A were mediated by 1) suppressing the activity of microglial NADPH oxidase and decreasing the production of reactive oxygen species, and 2) inhibiting NF-kappaB-mediated gene transcription of various proinflammatory mediators in microglia via IKK-beta suppression. These findings indicate that compound A afforded potent neuroprotection against LPS-induced neurodegeneration through selective inhibition of NF-kappaB activation and may be of potential benefit in the treatment of PD.
Figures
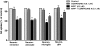
Similar articles
-
Resveratrol protects dopamine neurons against lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity through its anti-inflammatory actions.Mol Pharmacol. 2010 Sep;78(3):466-77. doi: 10.1124/mol.110.064535. Epub 2010 Jun 16. Mol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20554604 Free PMC article.
-
Squamosamide derivative FLZ protects dopaminergic neurons against inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration through the inhibition of NADPH oxidase activity.J Neuroinflammation. 2008 May 28;5:21. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-5-21. J Neuroinflammation. 2008. PMID: 18507839 Free PMC article.
-
Somatostatin prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced neurodegeneration in the rat substantia nigra by inhibiting the activation of microglia.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Jul;12(1):1002-8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3494. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25777539 Free PMC article.
-
NADPH oxidase mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity and proinflammatory gene expression in activated microglia.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jan 9;279(2):1415-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M307657200. Epub 2003 Oct 24. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14578353
-
The lipopolysaccharide Parkinson's disease animal model: mechanistic studies and drug discovery.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2008 Oct;22(5):453-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2008.00616.x. Epub 2008 Aug 15. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18710400 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CD11b/CD18 (Mac-1) is a novel surface receptor for extracellular double-stranded RNA to mediate cellular inflammatory responses.J Immunol. 2013 Jan 1;190(1):115-25. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202136. Epub 2012 Dec 3. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23209319 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol Produces Neurotrophic Effects on Cultured Dopaminergic Neurons through Prompting Astroglial BDNF and GDNF Release.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:937605. doi: 10.1155/2012/937605. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012. PMID: 23304227 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrahydroxystilbene Glucoside Produces Neuroprotection against 6-OHDA-Induced Dopamine Neurotoxicity.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Jan 14;2018:7927568. doi: 10.1155/2018/7927568. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 29576855 Free PMC article.
-
The endotoxin-induced neuroinflammation model of Parkinson's disease.Parkinsons Dis. 2011 Jan 18;2011:487450. doi: 10.4061/2011/487450. Parkinsons Dis. 2011. PMID: 21331154 Free PMC article.
-
HMGB1 acts on microglia Mac1 to mediate chronic neuroinflammation that drives progressive neurodegeneration.J Neurosci. 2011 Jan 19;31(3):1081-92. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3732-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21248133 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gao HM, Liu B, Zhang W, Hong JS. (2003a) Novel anti-inflammatory therapy for Parkinson's disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 24:395–401 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

