Kinetic characterization of the WalRKSpn (VicRK) two-component system of Streptococcus pneumoniae: dependence of WalKSpn (VicK) phosphatase activity on its PAS domain
- PMID: 20190050
- PMCID: PMC2863487
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01690-09
Kinetic characterization of the WalRKSpn (VicRK) two-component system of Streptococcus pneumoniae: dependence of WalKSpn (VicK) phosphatase activity on its PAS domain
Abstract
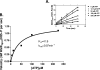
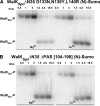
The WalRK two-component system plays important roles in maintaining cell wall homeostasis and responding to antibiotic stress in low-GC Gram-positive bacteria. In the major human pathogen, Streptococcus pneumoniae, phosphorylated WalR(Spn) (VicR) response regulator positively controls the transcription of genes encoding the essential PcsB division protein and surface virulence factors. WalR(Spn) is phosphorylated by the WalK(Spn) (VicK) histidine kinase. Little is known about the signals sensed by WalK histidine kinases. To gain information about WalK(Spn) signal transduction, we performed a kinetic characterization of the WalRK(Spn) autophosphorylation, phosphoryltransferase, and phosphatase reactions. We were unable to purify soluble full-length WalK(Spn). Consequently, these analyses were performed using two truncated versions of WalK(Spn) lacking its single transmembrane domain. The longer version (Delta35 amino acids) contained most of the HAMP domain and the PAS, DHp, and CA domains, whereas the shorter version (Delta195 amino acids) contained only the DHp and CA domains. The autophosphorylation kinetic parameters of Delta35 and Delta195 WalK(Spn) were similar [K(m)(ATP) approximately 37 microM; k(cat) approximately 0.10 min(-1)] and typical of those of other histidine kinases. The catalytic efficiency of the two versions of WalK(Spn) approximately P were also similar in the phosphoryltransfer reaction to full-length WalR(Spn). In contrast, absence of the HAMP-PAS domains significantly diminished the phosphatase activity of WalK(Spn) for WalR(Spn) approximately P. Deletion and point mutations confirmed that optimal WalK(Spn) phosphatase activity depended on the PAS domain as well as residues in the DHp domain. In addition, these WalK(Spn) DHp domain and DeltaPAS mutations led to attenuation of virulence in a murine pneumonia model.
Figures

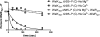

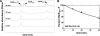

References
-
- Aiba, H., F. Nakasai, S. Mizushima, and T. Mizuno. 1989. Evidence for the physiological importance of the phosphotransfer between the two regulatory components, EnvZ and OmpR, in osmoregulation in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 264:14090-14094. - PubMed
-
- Alves, R., and M. A. Savageau. 2003. Comparative analysis of prototype two-component systems with either bifunctional or monofunctional sensors: differences in molecular structure and physiological function. Mol. Microbiol. 48:25-51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

