From combinatorial peptide selection to drug prototype (II): targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway
- PMID: 20190183
- PMCID: PMC2841862
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0915146107
From combinatorial peptide selection to drug prototype (II): targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway
Abstract
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), a tyrosine kinase, is central to human tumorigenesis. Typically, three classes of drugs inhibit tyrosine kinase pathways: blocking antibodies, small kinase inhibitors, and soluble ligand receptor traps/decoys. Only the first two types of EGFR-binding inhibitory drugs are clinically available; notably, no EGFR decoy has yet been developed. Here we identify small molecules mimicking EGFR and that functionally behave as soluble decoys for EGF and TGFalpha, ligands that would otherwise activate downstream signaling. After combinatorial library selection on EGFR ligands, a panel of binding peptides was narrowed by structure-function analysis. The most active motif was CVRAC (EGFR 283-287), which is necessary and sufficient for specific EGFR ligand binding. Finally, a synthetic retro-inverted derivative, (D)(CARVC), became our preclinical prototype of choice. This study reveals an EGFR-decoy drug candidate with translational potential.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
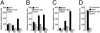
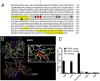

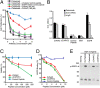

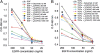
Similar articles
-
Peptide mimotopes recognized by antibodies cetuximab and matuzumab induce a functionally equivalent anti-EGFR immune response.Oncogene. 2010 Aug 12;29(32):4517-27. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.195. Epub 2010 May 31. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 20514015
-
Targeting the EGFR/PCNA signaling suppresses tumor growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells with cell-penetrating PCNA peptides.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 8;8(4):e61362. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061362. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23593472 Free PMC article.
-
Matuzumab and cetuximab activate the epidermal growth factor receptor but fail to trigger downstream signaling by Akt or Erk.Int J Cancer. 2008 Apr 1;122(7):1530-8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23253. Int J Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18033688
-
Overview of monoclonal antibodies and small molecules targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway in colorectal cancer.Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2005 Nov;5 Suppl 2:S71-80. doi: 10.3816/ccc.2005.s.010. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16336752 Review.
-
Cetuximab: an epidermal growth factor receptor chemeric human-murine monoclonal antibody.Drugs Today (Barc). 2005 Feb;41(2):107-27. doi: 10.1358/dot.2005.41.2.882662. Drugs Today (Barc). 2005. PMID: 15821783 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineered bivalent ligands to bias ErbB receptor-mediated signaling and phenotypes.J Biol Chem. 2011 Aug 5;286(31):27729-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.221093. Epub 2011 May 26. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21622572 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics resources and tools for phage display.Molecules. 2011 Jan 18;16(1):694-709. doi: 10.3390/molecules16010694. Molecules. 2011. PMID: 21245805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ligand-directed targeting of lymphatic vessels uncovers mechanistic insights in melanoma metastasis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Feb 24;112(8):2521-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1424994112. Epub 2015 Feb 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25659743 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal IgG in MGUS and multiple myeloma targets infectious pathogens.JCI Insight. 2017 Oct 5;2(19):e95367. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.95367. JCI Insight. 2017. PMID: 28978808 Free PMC article.
-
A neutralizing RNA aptamer against EGFR causes selective apoptotic cell death.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24071. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024071. Epub 2011 Sep 6. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21915281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gusterson BA, Hunter KD. Should we be surprised at the paucity of response to EGFR inhibitors? Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:522–527. - PubMed
-
- Baselga J. Targeting tyrosine kinases in cancer: The second wave. Science. 2006;312:1175–1178. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Mellinghoff IK, et al. Molecular determinants of the response of glioblastomas to EGFR kinase inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2012–2024. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

