Signatures of polycomb repression and reduced H3K4 trimethylation are associated with p15INK4b DNA methylation in AML
- PMID: 20190193
- PMCID: PMC2858468
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-233858
Signatures of polycomb repression and reduced H3K4 trimethylation are associated with p15INK4b DNA methylation in AML
Abstract
DNA hypermethylation of the p15INK4b tumor suppressor gene is commonly observed in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Repressive histone modifications and their associated binding proteins have been implicated in the regulation of DNA methylation and the transcriptional repression of genes with DNA methylation. We have used high-density chromatin immunoprecipitation-on-chip to determine the histone modifications that normally regulate p15INK4b expression in AML cells and how these marks are altered in cells that have p15INK4b DNA methylation. In AML patient blasts without p15INK4b DNA methylation, a bivalent pattern of active (H3K4me3) and repressive (H3K27me3) modifications exist at the p15INK4b promoter. AML patient blasts with p15INK4b DNA methylation lose H3K4me3 at p15INK4b and become exclusively marked by H3K27me3. H3K27me3, as well as EZH2, extends throughout p14ARF and p16INK4a, indicating that polycomb repression of p15INK4b is a common feature in all AML blasts irrespective of the DNA methylation status of the gene. Reactivation of p15INK4b expression in AML cell lines and patient blasts using 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine (decitabine) and trichostatin A increased H3K4me3 and maintained H3K27me3 enrichment at p15INK4b. These data indicate that AML cells with p15INK4b DNA methylation have an altered histone methylation pattern compared with unmethylated samples and that these changes are reversible by epigenetic drugs.
Figures

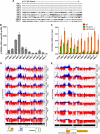
 , 10%-49% methylcytosine). (B-C) Quantitative reverse-transcriptase (RT)–PCR analysis of p15INK4b, p14ARF, and p16INK4a expression in AML cell lines. Copies of cDNA per 100 ng of total RNA were calculated from a plasmid DNA standard curve and represent the averages of 3 independent experiments with error bars of SD.
, 10%-49% methylcytosine). (B-C) Quantitative reverse-transcriptase (RT)–PCR analysis of p15INK4b, p14ARF, and p16INK4a expression in AML cell lines. Copies of cDNA per 100 ng of total RNA were calculated from a plasmid DNA standard curve and represent the averages of 3 independent experiments with error bars of SD.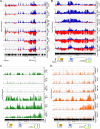
 , 10%-49% methylcytosine). (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of p15INK4b expression in AML patient blasts. cDNA copies per 50 ng total RNA were calculated from a plasmid DNA standard curve and represent the averages of 3 independent experiments with error bars of SD. Quantitative PCR analysis (C) of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 enrichment at the p15INK4b promoter. Data are averages of ΔΔCt compared with input DNA from 3 technical replicates with error bars of SD. ChIP-on-chip analysis of enrichment of H3K4me3 (blue) and H3K27me3 (red) on chromosome 9: 21953000 to 22003000 (D) and chromosome 9: 21990000 to 22003000 (E) in AML patient samples. Top axis represents H3K4me3; and bottom axis, H3K27me3. Normalized enrichment data (IP/input) are plotted on a log 2 scale.
, 10%-49% methylcytosine). (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of p15INK4b expression in AML patient blasts. cDNA copies per 50 ng total RNA were calculated from a plasmid DNA standard curve and represent the averages of 3 independent experiments with error bars of SD. Quantitative PCR analysis (C) of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 enrichment at the p15INK4b promoter. Data are averages of ΔΔCt compared with input DNA from 3 technical replicates with error bars of SD. ChIP-on-chip analysis of enrichment of H3K4me3 (blue) and H3K27me3 (red) on chromosome 9: 21953000 to 22003000 (D) and chromosome 9: 21990000 to 22003000 (E) in AML patient samples. Top axis represents H3K4me3; and bottom axis, H3K27me3. Normalized enrichment data (IP/input) are plotted on a log 2 scale.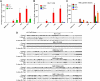
 , 10%-49% methylcytosine).
, 10%-49% methylcytosine).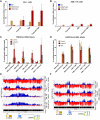
References
-
- Herman JG, Civin CI, Issa JP, Collector MI, Sharkis SJ, Baylin SB. Distinct patterns of inactivation of p15INK4B and p16INK4A characterize the major types of hematological malignancies. Cancer Res. 1997;57(5):837–841. - PubMed
-
- Drexler HG. Review of alterations of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor INK4 family genes p15, p16, p18 and p19 in human leukemia-lymphoma cells. Leukemia. 1998;12(6):845–859. - PubMed
-
- Sherr CJ, Roberts JM. CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev. 1999;13(12):1501–1512. - PubMed
-
- Hannon GJ, Beach D. p15INK4B is a potential effector of TGF-beta-induced cell cycle arrest. Nature. 1994;371(6494):257–261. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt M, Bies J, Tamura T, Ozato K, Wolff L. The interferon regulatory factor ICSBP/IRF-8 in combination with PU.1 up-regulates expression of tumor suppressor p15(Ink4b) in murine myeloid cells. Blood. 2004;103(11):4142–4149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

