Evaluation of CT perfusion in the setting of cerebral ischemia: patterns and pitfalls
- PMID: 20190208
- PMCID: PMC7965002
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A2026
Evaluation of CT perfusion in the setting of cerebral ischemia: patterns and pitfalls
Abstract
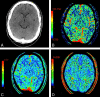
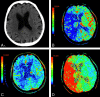
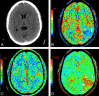
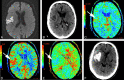
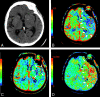
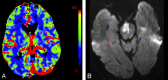
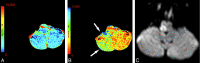
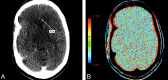
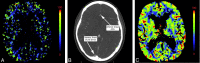
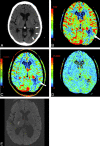
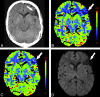
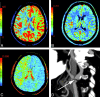
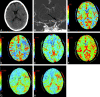
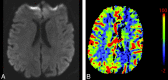
CTP has a growing role in evaluating stroke. It can be performed immediately following NCCT and has advantages of accessibility and speed. Differentiation of salvageable ischemic penumbra from unsalvageable core infarct may help identify patients most likely to benefit from thrombectomy or thrombolysis. Still, CTP interpretation can be complex. We review normal and ischemic perfusion patterns followed by an illustrative series of technical/diagnostic challenges of CTP interpretation in the setting of acute stroke syndromes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimal thresholds for ischemic penumbra predicted by computed tomography perfusion in patients with acute ischemic stroke treated with mechanical thrombectomy.J Neurointerv Surg. 2018 Mar;10(3):279-284. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2017-013083. Epub 2017 Jun 9. J Neurointerv Surg. 2018. PMID: 28600481
-
Perfusion computed tomography thresholds defining ischemic penumbra and infarct core: studies in a rat stroke model.Int J Stroke. 2015 Jun;10(4):553-9. doi: 10.1111/ijs.12147. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Int J Stroke. 2015. PMID: 24138577
-
Theoretic basis and technical implementations of CT perfusion in acute ischemic stroke, part 2: technical implementations.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009 May;30(5):885-92. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1492. Epub 2009 Mar 19. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009. PMID: 19299489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Admission CT perfusion may overestimate initial infarct core: the ghost infarct core concept.J Neurointerv Surg. 2017 Jan;9(1):66-69. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2016-012494. Epub 2016 Aug 26. J Neurointerv Surg. 2017. PMID: 27566491
-
"Code-Stroke" CT Perfusion; Challenges and Pitfalls.Acad Radiol. 2019 Nov;26(11):1565-1579. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2018.12.013. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Acad Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30655051 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurovascular emergencies: imaging diagnosis and neurointerventional treatment.Emerg Radiol. 2017 Apr;24(2):183-193. doi: 10.1007/s10140-016-1450-x. Epub 2016 Oct 7. Emerg Radiol. 2017. PMID: 27718098 Review.
-
A novel computed tomography perfusion-based quantitative tool for evaluation of perfusional abnormalities in migrainous aura stroke mimic.Neurol Sci. 2020 Nov;41(11):3321-3328. doi: 10.1007/s10072-020-04476-5. Epub 2020 May 26. Neurol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32458253
-
Research progress of imaging technologies for ischemic cerebrovascular diseases.J Int Med Res. 2021 Mar;49(3):300060520972601. doi: 10.1177/0300060520972601. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33730890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence for localization of the acute ischemic stroke by non-contrast computed tomography.PLoS One. 2022 Dec 1;17(12):e0277573. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277573. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36454916 Free PMC article.
-
TMS-Induced Central Motor Conduction Time at the Non-Infarcted Hemisphere Is Associated with Spontaneous Motor Recovery of the Paretic Upper Limb after Severe Stroke.Brain Sci. 2021 May 15;11(5):648. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11050648. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 34063558 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Lucas EM, Sanchez E, Gutierrez A, et al. . CT protocol for acute stroke: tips and tricks for general radiologists. Radiographics 2008; 28: 1673– 87 - PubMed
-
- Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke: The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. N Engl J Med 1995; 333: 1581– 87 - PubMed
-
- Dzialowski I, Hill MD, Coutts SB, et al. . Extent of early ischemic changes on computed tomography (CT) before thrombolysis: prognostic value of the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score in ECASS II. Stroke 2006; 37: 973– 78. Epub 2006 Feb 23 - PubMed
-
- Furlan A, Higashida R, Wechsler L, et al. . Intra-arterial prourokinase for acute ischemic stroke: the PROACT II study—a randomized controlled trial. Prolyse in Acute Cerebral Thromboembolism. JAMA 1999; 282: 2003– 11 - PubMed
-
- Schramm P, Schellinger PD, Klotz E, et al. . Comparison of perfusion computed tomography and computed tomography angiography source images with perfusion-weighted imaging and diffusion-weighted imaging in patients with acute stroke of less than 6 hours' duration. Stroke 2004; 35: 1652– 58 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
