The VEGF family in cancer and antibody-based strategies for their inhibition
- PMID: 20190566
- PMCID: PMC2840235
- DOI: 10.4161/mabs.2.2.11360
The VEGF family in cancer and antibody-based strategies for their inhibition
Abstract
Angiogenesis is required in normal physiological processes, but is also involved in tumor growth, progression and metastasis. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a primary mediator of angiogenesis in normal physiology and in disease, and other VEGF family members and their receptors provide targets that have been explored extensively for cancer therapy. Small molecule inhibitors and antibody/protein-based strategies that target the VEGF pathway have been studied in multiple types of cancer. This review will focus on VEGF pathway targeting antibodies that are currently being evaluated in pre-clinical and clinical studies.
Figures
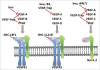

References
-
- Roskoski R., Jr Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling in tumor progression. Crit Rev in Oncol Hematol. 2007;62:179–213. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev. 2004;25:581–611. - PubMed
-
- Hoeben A, Landuyt B, Highley MS, Wildiers H, Van Oosterom AT, De Bruijn EA. Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis. Pharmacol Rev. 2004;56:549–580. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Folkman J. Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell. 1996;86:353–364. - PubMed
-
- Gerwins P, Skoldenberg E, Claesson-Welsh L. Function of fibroblast growth factors and vascular endothelial growth factors and their receptors in angiogenesis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2000;34:185–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
