Unique autoreactive T cells recognize insulin peptides generated within the islets of Langerhans in autoimmune diabetes
- PMID: 20190756
- PMCID: PMC3080751
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1850
Unique autoreactive T cells recognize insulin peptides generated within the islets of Langerhans in autoimmune diabetes
Abstract
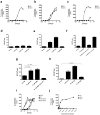
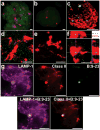
In addition to the genetic framework, there are two other critical requirements for the development of tissue-specific autoimmune disease. First, autoreactive T cells need to escape thymic negative selection. Second, they need to find suitable conditions for autoantigen presentation and activation in the target tissue. We show here that these two conditions are fulfilled in diabetic mice of the nonobese diabetic (NOD) strain. A set of autoreactive CD4(+) T cells specific for an insulin peptide, with the noteworthy feature of not recognizing the insulin protein when processed by antigen-presenting cells (APCs), escaped thymic control, participated in diabetes and caused disease. Moreover, APCs in close contact with beta cells in the islets of Langerhans bore vesicles with the antigenic insulin peptides and activated peptide-specific T cells. Our findings may be relevant for other cases of endocrine autoimmunity.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson MS, Bluestone JA. The NOD mouse: a model of immune disregulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:447–485. - PubMed
-
- Wegmann DR, Norbury-Glaser M, Daniel D. Insulin-specific T cells are a predominant component of islet infiltrates in pre-diabetic NOD mice. Eur J Immunol. 1994;24:1853–1857. - PubMed
-
- Wegmann DR, Gill RG, Norbury-Glaser M, Schloot N, Daniel D. Analysis of the spontaneous T cell response to insulin in NOD mice. J Autoimmun. 1994;7:833–843. - PubMed
-
- Daniel D, Gill RG, Schloot N, Wegmann D. Epitope specificity, cytokine production profile and diabetogenic activity of insulin-specific T cell clones isolated from NOD mice. Eur J Immunol. 1995;25:1056–1062. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

