Kynurenine is an endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced during inflammation
- PMID: 20190767
- PMCID: PMC3556275
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2092
Kynurenine is an endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced during inflammation
Erratum in
- Nat Med. 2010 May;16(5):607
Abstract
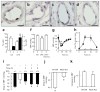
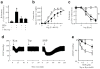
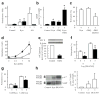
Control of blood vessel tone is central to vascular homeostasis. Here we show that metabolism of tryptophan to kynurenine by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (Ido) expressed in endothelial cells contributes to arterial vessel relaxation and the control of blood pressure. Infection of mice with malarial parasites (Plasmodium berghei) or induction of endotoxemia in mice led to endothelial expression of Ido, decreased plasma tryptophan concentration, increased kynurenine concentration and hypotension. Pharmacological inhibition of Ido increased blood pressure in systemically inflamed mice but not in mice deficient in Ido or interferon-gamma, which is required for Ido induction. Both tryptophan and kynurenine dilated preconstricted porcine coronary arteries; the dilating effect of tryptophan required the presence of active Ido and an intact endothelium, whereas the effect of kynurenine was endothelium independent. The arterial relaxation induced by kynurenine was mediated by activation of the adenylate and soluble guanylate cyclase pathways. Kynurenine administration decreased blood pressure in a dose-dependent manner in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Our results identify tryptophan metabolism by Ido as a new pathway contributing to the regulation of vascular tone.
Figures

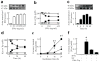
Comment in
-
Ido brings down the pressure in systemic inflammation.Nat Med. 2010 Mar;16(3):265-7. doi: 10.1038/nm0310-265. Nat Med. 2010. PMID: 20208509 No abstract available.
References
-
- Riedemann NC, Guo RF, Ward PA. Novel strategies for the treatment of sepsis. Nature Medicine. 2003;9:517–523. - PubMed
-
- Gomez-Jimenez J, et al. L-arginine: nitric oxide pathway in endotoxemia and human septic shock. Crit Care Med. 1995;23:253–258. - PubMed
-
- Ignarro LJ, Cirino G, Casini A, Napoli C. Nitric oxide as a signaling molecule in the vascular system: an overview. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1999;34:879–886. - PubMed
-
- Meyer J, et al. Reversal of hyperdynamic response to continuous endotoxin administration by inhibition of NO synthesis. J Appl Physiol. 1992;73:324–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

