Do children prefer contingencies? An evaluation of the efficacy of and preference for contingent versus noncontingent social reinforcement during play
- PMID: 20190915
- PMCID: PMC2741068
- DOI: 10.1901/jaba.2009.42-511
Do children prefer contingencies? An evaluation of the efficacy of and preference for contingent versus noncontingent social reinforcement during play
Abstract
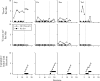
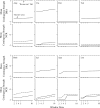
Discovering whether children prefer reinforcement via a contingency or independent of their behavior is important considering the ubiquity of these programmed schedules of reinforcement. The current study evaluated the efficacy of and preference for social interaction within differential reinforcement of alternative behavior (DRA) and noncontingent reinforcement (NCR) schedules with typically developing children. Results showed that 7 of the 8 children preferred the DRA schedule; 1 child was indifferent. We also demonstrated a high degree of procedural fidelity, which suggested that preference is influenced by the presence of a contingency under which reinforcement can be obtained. These findings are discussed in terms of (a) the selection of reinforcement schedules in practice, (b) variables that influence children's preferences for contexts, and (c) the selection of experimental control procedures when evaluating the effects of reinforcement.
Keywords: concurrent-chains arrangement; contingency strength; differential reinforcement; noncontingent reinforcement; preference assessment.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Examining the generality of children's preference for contingent reinforcement via extension to different responses, reinforcers, and schedules.J Appl Behav Anal. 2010 Fall;43(3):397-409. doi: 10.1901/jaba.2010.43-397. J Appl Behav Anal. 2010. PMID: 21358901 Free PMC article.
-
How should periods without social interaction be scheduled? Children's preference for practical schedules of positive reinforcement.J Appl Behav Anal. 2014 Fall;47(3):500-22. doi: 10.1002/jaba.140. Epub 2014 Jun 3. J Appl Behav Anal. 2014. PMID: 24890928
-
Noncontingent reinforcement without extinction plus differential reinforcement of alternative behavior during treatment of problem behavior.J Appl Behav Anal. 2017 Jul;50(3):590-599. doi: 10.1002/jaba.395. Epub 2017 May 17. J Appl Behav Anal. 2017. PMID: 28513826
-
A review of "noncontingent" reinforcement as treatment for the aberrant behavior of individuals with developmental disabilities.Res Dev Disabil. 2000 Sep-Oct;21(5):377-91. doi: 10.1016/s0891-4222(00)00050-0. Res Dev Disabil. 2000. PMID: 11100801 Review.
-
Applying Standards of Effectiveness to Noncontingent Reinforcement: A Systematic Literature Review.Behav Modif. 2021 Jul;45(4):619-640. doi: 10.1177/0145445519865073. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Behav Modif. 2021. PMID: 31452379
Cited by
-
Choice versus no choice: Practical considerations for increasing choices.J Appl Behav Anal. 2025 Jan;58(1):100-117. doi: 10.1002/jaba.2920. Epub 2024 Nov 12. J Appl Behav Anal. 2025. PMID: 39532823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bridging the gap between laboratory and applied research on response-independent schedules.J Appl Behav Anal. 2023 Jan;56(1):55-77. doi: 10.1002/jaba.965. Epub 2022 Nov 28. J Appl Behav Anal. 2023. PMID: 36440664 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the value of choice in a token system.J Appl Behav Anal. 2010 Fall;43(3):553-7. doi: 10.1901/jaba.2010.43-553. J Appl Behav Anal. 2010. PMID: 21358919 Free PMC article.
-
Contingency Enhances Sensitivity to Loss in a Gambling Task with Diminishing Returns.Psychol Rec. 2016 Jun;66(2):301-308. doi: 10.1007/s40732-016-0172-5. Epub 2016 Feb 24. Psychol Rec. 2016. PMID: 27182088 Free PMC article.
-
An Application of the Group-Oriented Concurrent-Chains Arrangement.Behav Anal Pract. 2018 Sep 20;12(2):310-319. doi: 10.1007/s40617-018-00286-6. eCollection 2019 Jun. Behav Anal Pract. 2018. PMID: 31976236 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

