Tuning and fine-tuning of synapses with adenosine
- PMID: 20190960
- PMCID: PMC2769002
- DOI: 10.2174/157015909789152128
Tuning and fine-tuning of synapses with adenosine
Abstract
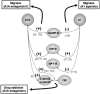
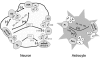
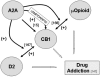
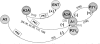
The 'omnipresence' of adenosine in all nervous system cells (neurons and glia) together with the intensive release of adenosine following insults, makes adenosine as a sort of 'maestro' of synapses leading to the homeostatic coordination of brain function. Besides direct actions of adenosine on the neurosecretory mechanisms, where adenosine operates to tune neurotransmitter release, receptor-receptor interactions as well as interplays between adenosine receptors and transporters occur as part of the adenosine's attempt to fine tuning synaptic transmission. This review will focus on the different ways adenosine can use to trigger or brake the action of several neurotransmitters and neuromodulators. Adenosine receptors cross talk with other G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), with ionotropic receptors and with receptor kinases. Most of these interactions occur through A2A receptors, which in spite their low density in some brain areas, such as the hippocampus, may function as metamodulators. Tonic adenosine A2A receptor activity is a required step to allow synaptic actions of neurotrophic factors, namely upon synaptic transmission at both pre- and post-synaptic level as well as upon synaptic plasticity and neuronal survival. The implications of these interactions in normal brain functioning and in neurologic and psychiatric dysfunction will be discussed.
Keywords: Adenosine; G protein coupled receptors; epilepsy; ionotropic receptors; metamodulation; neurodegenerative diseases; receptor cross-talk; receptor kinases..
Figures
References
-
- Abbracchio MP, Fogliatto G, Paoletti AM, Rovati GE, Cattabeni F. Prolonged in vitro exposure of rat brain slices to adenosine analogues: selective desensitization of A1 but not A2 receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1992;227:317–324. - PubMed
-
- Adams CL, Cowen MS, Short JL, Lawrence AJ. Combined antagonism of glutamate mGlu5 and adenosine A2A receptors interact to regulate alcohol-seeking in rats. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008;11:229–241. - PubMed
-
- Alexander SP, Curtis AR, Hill SJ, Kendall DA. Activation of a metabotropic excitatory aminoacid receptor potentiates A2b adenosine receptor-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation. Neurosci. Lett. 1992;146:231–233. - PubMed
-
- Alexander S P, Reddington M. The cellular localization of adenosine receptors in rat neostriatum. Neuroscience. 1989;28:645–551. - PubMed
-
- Andersson M, Usiello A, Borgkvist A, Pozzi L, Dominguez C, Fienberg AA, Svenningsson P, Fredholm BB, Borrelli E, Greengard P, Fisone G. Cannabinoid action depends on phosphorylation of dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein of 32 kDa at the protein kinase A site in striatal projection neurons. J. Neurosci. 2005;25:8432–8438. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
