Adenosine neuromodulation and traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 20190964
- PMCID: PMC2769006
- DOI: 10.2174/157015909789152137
Adenosine neuromodulation and traumatic brain injury
Abstract
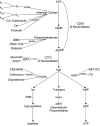
Adenosine is a ubiquitous signaling molecule, with widespread activity across all organ systems. There is evidence that adenosine regulation is a significant factor in traumatic brain injury (TBI) onset, recovery, and outcome, and a growing body of experimental work examining the therapeutic potential of adenosine neuromodulation in the treatment of TBI. In the central nervous system (CNS), adenosine (dys)regulation has been demonstrated following TBI, and correlated to several TBI pathologies, including impaired cerebral hemodynamics, anaerobic metabolism, and inflammation. In addition to acute pathologies, adenosine function has been implicated in TBI comorbidities, such as cognitive deficits, psychiatric function, and post-traumatic epilepsy. This review presents studies in TBI as well as adenosine-related mechanisms in co-morbidities of and unfavorable outcomes resulting from TBI. While the exact role of the adenosine system following TBI remains unclear, there is increasing evidence that a thorough understanding of adenosine signaling will be critical to the development of diagnostic and therapeutic tools for the treatment of TBI.
Keywords: Adenosine deaminase; adenosine kinase; caffeine; comorbidity.; nucleoside transport; nucleotidase.
Figures
References
-
- Abbott CA, Baker E, Sutherland GR, McCaughan GW. Genomic organization, exact localization, and tissue expression of the human CD26 (dipeptidyl peptidase IV) gene. Immunogenetics. 1994;40:331–338. - PubMed
-
- Abrams TW. Cyclic AMP (cAMP) Role in Learning and Memory. In: Squire LR, editor. Encyclopedia of Neuroscience. Oxford: Academic Press; 2009. pp. 265–277.
-
- Al Moutaery K, Al Deeb S, Ahmad Khan H, Tariq M. Caffeine impairs short-term neurological outcome after concussive head injury in rats. Neurosurgery. 2003;53:704–711. discussion 711-702. - PubMed
-
- Almeida T, Rodrigues RJ, de Mendonca A, Ribeiro JA, Cunha RA. Purinergic P2 receptors trigger adenosine release leading to adenosine A2A receptor activation and facilitation of long-term potentiation in rat hippocampal slices. Neuroscience. 2003;122:111–121. - PubMed
-
- Antoni FA. Molecular diversity of cyclic AMP signalling. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2000;21:103–132. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials