Balloon dilatation for corrosive esophageal strictures in children: radiologic and clinical outcomes
- PMID: 20191068
- PMCID: PMC2827784
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2010.11.2.203
Balloon dilatation for corrosive esophageal strictures in children: radiologic and clinical outcomes
Abstract
Objective: We retrospectively evaluated the effectiveness of the esophageal balloon dilatation (EBD) in children with a corrosive esophageal stricture.
Materials and methods: The study subjects included 14 patients (M:F = 8:6, age range: 17-85 months) who underwent an EBD due to a corrosive esophageal stricture. The causative agents for the condition were glacial acetic acid (n = 9) and lye (n = 5).
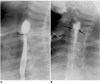
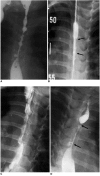
Results: A total of 52 EBD sessions were performed in 14 patients (range 1-8 sessions). During the mean 15-month follow-up period (range 1-79 months), 12 patients (86%) underwent additional EBD due to recurrent esophageal stricture. Dysphagia improved after each EBD session and oral feeding was possible between EBD sessions. Long-term success (defined as dysphagia relief for at least 12 months after the last EBD) was achieved in two patients (14%). Temporary success of EBD (defined as dysphagia relief for at least one month after the EBD session) was achieved in 17 out of 52 sessions (33%). A submucosal tear of the esophagus was observed in two (4%) sessions of EBD.
Conclusion: Only a limited number of children with corrosive esophageal strictures were considered cured by EBD. However, the outcome of repeated EBD was sufficient to allow the children to eat per os prior to surgical management.
Keywords: Balloon dilatation; Children; Corrosive esophagitis; Dysphagia; Esophageal stricture; Esophagus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fluoroscopic balloon dilatation for caustic esophageal stricture in children: an 8-year experience.J Pediatr Surg. 2013 Nov;48(11):2230-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2013.04.005. J Pediatr Surg. 2013. PMID: 24210191
-
Oesophageal strictures caused by the ingestion of corrosive agents: effectiveness of balloon dilatation in children.Clin Radiol. 2009 Mar;64(3):265-71. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2008.10.001. Epub 2008 Nov 18. Clin Radiol. 2009. PMID: 19185656
-
Effectiveness of endoscopic balloon dilatation in grade 2a and 2b esophageal burns in children.Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2017 Oct;26(5):300-306. doi: 10.1080/13645706.2017.1298621. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2017. PMID: 28281403
-
Endoscopic balloon dilatation of esophageal strictures in infants and children: 17 years' experience and a literature review.J Pediatr Surg. 2003 Dec;38(12):1712-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2003.08.040. J Pediatr Surg. 2003. PMID: 14666449 Review.
-
Corrosive ingestion managements in children.Esophagus. 2020 Oct;17(4):365-375. doi: 10.1007/s10388-020-00745-6. Epub 2020 May 5. Esophagus. 2020. PMID: 32372308 Review.
Cited by
-
Corrosive upper gastrointestinal strictures in children: Difficulties and dilemmas.World J Clin Pediatr. 2021 Nov 9;10(6):124-136. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v10.i6.124. eCollection 2021 Nov 9. World J Clin Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34868889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outcomes of pneumatic dilation in pediatric caustic esophageal strictures: a descriptive and analytic study from a developing country.Surg Endosc. 2023 Dec;37(12):9291-9298. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-10489-w. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Surg Endosc. 2023. PMID: 37884732
-
Individually designed fully covered self-expandable metal stents for pediatric refractory benign esophageal strictures.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 19;11(1):22575. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01921-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34799603 Free PMC article.
-
Step-Down Approach for Pharyngoesophageal Corrosive Stricture: Outcome and Analysis.World J Surg. 2017 Aug;41(8):2053-2061. doi: 10.1007/s00268-017-3966-y. World J Surg. 2017. PMID: 28265737
-
Factors influencing outcomes of esophageal balloon dilatation for anastomosis site stenosis after esophageal atresia surgery.Pediatr Radiol. 2023 Mar;53(3):349-357. doi: 10.1007/s00247-022-05523-3. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Pediatr Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36216986
References
-
- Huang YC, Ni YH, Lai HS, Chang MH. Corrosive esophagitis in children. Pediatr Surg Int. 2004;20:207–210. - PubMed
-
- Song HY, Han YM, Kim HN, Kim CS, Choi KC. Corrosive esophageal stricture: safety and effectiveness of balloon dilation. Radiology. 1992;184:373–378. - PubMed
-
- Park JY, Shin JY, Yang HR, Ko JS, Kim WS, Seo JK. Usefulness of early endoscopy for predicting the development of stricture after corrosive esophagitis in children. Korean J Pediatr. 2009;52:446–452.
-
- Hamza AF, Abdelhay S, Sherif H, Hasan T, Soliman H, Kabesh A, et al. Caustic esophageal strictures in children: 30 years' experience. J Pediatr Surg. 2003;38:828–833. - PubMed
-
- Weintraub JL, Eubig J. Balloon catheter dilatation of benign esophageal strictures in children. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006;17:831–835. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

