Adenosyl radical: reagent and catalyst in enzyme reactions
- PMID: 20191656
- PMCID: PMC3011887
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.200900777
Adenosyl radical: reagent and catalyst in enzyme reactions
Abstract
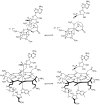
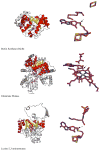
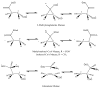
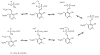
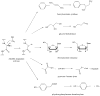
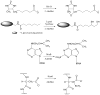
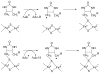
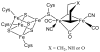
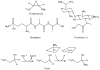
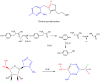
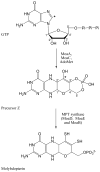
Adenosine is undoubtedly an ancient biological molecule that is a component of many enzyme cofactors: ATP, FADH, NAD(P)H, and coenzyme A, to name but a few, and, of course, of RNA. Here we present an overview of the role of adenosine in its most reactive form: as an organic radical formed either by homolytic cleavage of adenosylcobalamin (coenzyme B(12), AdoCbl) or by single-electron reduction of S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet) complexed to an iron-sulfur cluster. Although many of the enzymes we discuss are newly discovered, adenosine's role as a radical cofactor most likely arose very early in evolution, before the advent of photosynthesis and the production of molecular oxygen, which rapidly inactivates many radical enzymes. AdoCbl-dependent enzymes appear to be confined to a rather narrow repertoire of rearrangement reactions involving 1,2-hydrogen atom migrations; nevertheless, mechanistic insights gained from studying these enzymes have proved extremely valuable in understanding how enzymes generate and control highly reactive free radical intermediates. In contrast, there has been a recent explosion in the number of radical-AdoMet enzymes discovered that catalyze a remarkably wide range of chemically challenging reactions; here there is much still to learn about their mechanisms. Although all the radical-AdoMet enzymes so far characterized come from anaerobically growing microbes and are very oxygen sensitive, there is tantalizing evidence that some of these enzymes might be active in aerobic organisms including humans.
Figures
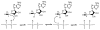
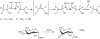
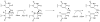
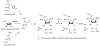

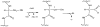
Similar articles
-
Radical mechanisms in adenosylmethionine- and adenosylcobalamin-dependent enzymatic reactions.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000 Oct 1;382(1):6-14. doi: 10.1006/abbi.2000.2010. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000. PMID: 11051091 Review.
-
Radical mechanisms of enzymatic catalysis.Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:121-48. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.70.1.121. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11395404 Review.
-
Paradigm Shift for Radical S-Adenosyl-l-methionine Reactions: The Organometallic Intermediate Ω Is Central to Catalysis.J Am Chem Soc. 2018 Jul 18;140(28):8634-8638. doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b04061. Epub 2018 Jul 6. J Am Chem Soc. 2018. PMID: 29954180 Free PMC article.
-
Radical use of Rossmann and TIM barrel architectures for controlling coenzyme B12 chemistry.Annu Rev Biophys. 2012;41:403-27. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-050511-102225. Annu Rev Biophys. 2012. PMID: 22577824 Review.
-
Adenosylcobalamin enzymes: theory and experiment begin to converge.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Nov;1824(11):1154-64. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.03.012. Epub 2012 Apr 3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22516318 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Viperin: An ancient radical SAM enzyme finds its place in modern cellular metabolism and innate immunity.J Biol Chem. 2020 Aug 14;295(33):11513-11528. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.012784. Epub 2020 Jun 16. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32546482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revealing nature's synthetic potential through the study of ribosomal natural product biosynthesis.ACS Chem Biol. 2013 Mar 15;8(3):473-87. doi: 10.1021/cb3005325. Epub 2013 Jan 8. ACS Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23286465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probing reversible chemistry in coenzyme B12 -dependent ethanolamine ammonia lyase with kinetic isotope effects.Chemistry. 2015 Jun 8;21(24):8826-31. doi: 10.1002/chem.201500958. Epub 2015 May 7. Chemistry. 2015. PMID: 25950663 Free PMC article.
-
The mononuclear molybdenum enzymes.Chem Rev. 2014 Apr 9;114(7):3963-4038. doi: 10.1021/cr400443z. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Chem Rev. 2014. PMID: 24467397 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
The enzyme-mediated direct reversal of a dithymine photoproduct in germinating endospores.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jun 25;14(7):13137-53. doi: 10.3390/ijms140713137. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23799365 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

