Colon cancer treatment costs for Medicare and dually eligible beneficiaries
- PMID: 20191756
- PMCID: PMC2832226
Colon cancer treatment costs for Medicare and dually eligible beneficiaries
Abstract
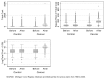
To estimate the cost attributable to colon cancer treatment 1 year after diagnosis by cancer stage, comorbidity, treatment regimen, and Medicaid eligibility, we extracted an inception cohort of colon cancer patients aged 66 and older diagnosed between 1997 and 2000 from the Michigan Tumor Registry. Patients were matched to non-cancer control subjects in the Medicare Denominator file. We used the difference-in-differences method to estimate costs attributable to cancer, controlling for costs prior to diagnosis. The mean total colon cancer cost per Medicare patient was $29,196. The method can be applied to longitudinal data to estimate long term costs of cancer from inception where incident patients are identified from a tumor registry.
Figures
References
-
- Barlow WE, Ichikawa L, Rosner D, et al. Analysis of Case-Cohort Designs. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 1999;52(12):1165–1172. - PubMed
-
- Basu A, Rathouz PJ. Estimating Marginal and Incremental Effects on Health Outcomes Using Flexible Link and Variance Function Models. Biostatistics. 2005;6(1):93–109. - PubMed
-
- Bradley CJ, Gardiner J, Given CW, et al. Cancer, Medicaid Enrollment, and Survival Disparities. Cancer. 2005;103(8):1712–1718. - PubMed
-
- Bradley CJ, Given CW, Luo Z, et al. Medicaid, Medicare, and the Michigan Tumor Registry: A Linkage Strategy. Medical Decision Making. 2007;27(4):352–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical