Phase separation in biological membranes: integration of theory and experiment
- PMID: 20192775
- PMCID: PMC3694198
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.093008.131238
Phase separation in biological membranes: integration of theory and experiment
Abstract
Lipid bilayer model membranes that contain a single lipid species can undergo transitions between ordered and disordered phases, and membranes that contain a mixture of lipid species can undergo phase separations. Studies of these transformations are of interest for what they can tell us about the interaction energies of lipid molecules of different species and conformations. Nanoscopic phases (<200 nm) can provide a model for membrane rafts, specialized membrane domains enriched in cholesterol and sphingomyelin, which are believed to have essential biological functions in cell membranes. Crucial questions are whether lipid nanodomains can exist in stable equilibrium in membranes and what is the distribution of their sizes and lifetimes in membranes of different composition. Theoretical methods have supplied much information on these questions, but better experimental methods are needed to detect and characterize nanodomains under normal membrane conditions. This review summarizes linkages between theoretical and experimental studies of phase separation in lipid bilayer model membranes.
Figures
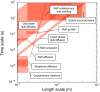

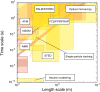
References
-
- Anderson RG, Jacobson K. A role for lipid shells in targeting proteins to caveolae, rafts, and other lipid domains. Science. 2002;296:1821. - PubMed
-
- Ayton G, Bardenhagen SG, McMurtry P, Sulsky D, Voth GA. Interfacing continuum and molecular dynamics: an application to lipid bilayers. The Journal of Chemical Physics. 2001;114:6913.
-
- Baumgart T, Hess ST, Webb WW. Imaging coexisting fluid domains in biomembrane models coupling curvature and line tension. Nature. 2003;425:821. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

