The U1-snRNP complex: structural properties relating to autoimmune pathogenesis in rheumatic diseases
- PMID: 20192997
- PMCID: PMC3074261
- DOI: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2009.00863.x
The U1-snRNP complex: structural properties relating to autoimmune pathogenesis in rheumatic diseases
Abstract
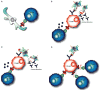
The U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle (snRNP) is a target of autoreactive B cells and T cells in several rheumatic diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD). We propose that inherent structural properties of this autoantigen complex, including common RNA-binding motifs, B and T-cell epitopes, and a unique stimulatory RNA molecule, underlie its susceptibility as a target of the autoimmune response. Immune mechanisms that may contribute to overall U1-snRNP immunogenicity include epitope spreading through B and T-cell interactions, apoptosis-induced modifications, and toll-like receptor (TLR) activation through stimulation by U1-snRNA. We conclude that understanding the interactions between U1-snRNP and the immune system will provide insights into why certain patients develop anti-U1-snRNP autoimmunity, and more importantly how to effectively target therapies against this autoimmune response.
Figures

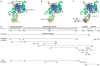
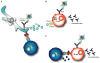
References
-
- von Muhlen CA, Tan EM. Autoantibodies in the diagnosis of systemic rheumatic diseases. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1995;24:323–358. - PubMed
-
- Tan EM, Kunkel HG. Characteristics of a soluble nuclear antigen precipitating with sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1966;96:464–471. - PubMed
-
- van Venrooij WJ, Zendman AJ, Pruijn GJ. Autoantibodies to citrullinated antigens in (early) rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2006;6:37–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

