Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 20193003
- PMCID: PMC2913689
- DOI: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2009.00859.x
Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
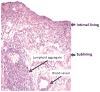
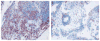
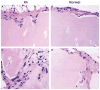
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) remains a significant unmet medical need despite significant therapeutic advances. The pathogenesis of RA is complex and includes many cell types, including T cells, B cells, and macrophages. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) in the synovial intimal lining also play a key role by producing cytokines that perpetuate inflammation and proteases that contribute to cartilage destruction. Rheumatoid FLS develop a unique aggressive phenotype that increases invasiveness into the extracellular matrix and further exacerbates joint damage. Recent advances in understanding the biology of FLS, including their regulation regulate innate immune responses and activation of intracellular signaling mechanisms that control their behavior, provide novel insights into disease mechanisms. New agents that target FLS could potentially complement the current therapies without major deleterious effect on adaptive immune responses.
Figures
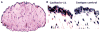
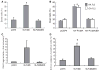
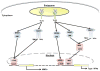
References
-
- Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423:356–361. - PubMed
-
- Bresnihan B, Flanagan AM. Synovium. In: Firestein GS, Budd RC, Harris T, McInnes IB, Ruddy S, Sergent JS, editors. Kelly’s Textbook of Rheumatology. 8. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2009. pp. 23–37.
-
- Firestein GS. Invasive fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Passive responders or transformed aggressors? Arthritis Rheum. 1996;39:1781–1790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

