The inhaled phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor GSK256066 reduces allergen challenge responses in asthma
- PMID: 20193079
- PMCID: PMC2841147
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-11-26
The inhaled phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor GSK256066 reduces allergen challenge responses in asthma
Abstract
GSK256066 is a selective phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor that can be given by inhalation, minimising the potential for side effects. We evaluated the effects of GSK256066 on airway responses to allergen challenge in mild asthmatics.
Methods: In a randomised, double blind, cross-over study, 24 steroid naive atopic asthmatics with both early (EAR) and late (LAR) responses to inhaled allergen received inhaled GSK256066 87.5 mcg once per day and placebo for 7 days, followed by allergen challenge. Methacholine reactivity was measured 24 h post-allergen. Plasma pharmacokinetics were measured. The primary endpoint was the effect on LAR.
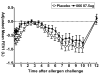
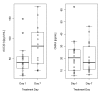
Results: GSK256066 significantly reduced the LAR, attenuating the fall in minimum and weighted mean FEV1 by 26.2% (p = 0.007) and 34.3% (p = 0.005) respectively compared to placebo. GSK256066 significantly reduced the EAR, inhibiting the fall in minimum and weighted mean FEV1 by 40.9% (p = 0.014) and 57.2% (p = 0.014) respectively compared to placebo. There was no effect on pre-allergen FEV1 or methacholine reactivity post allergen. GSK256066 was well tolerated, with low systemic exposure; plasma levels were not measurable after 4 hours in the majority of subjects.
Conclusions: GSK256066 demonstrated a protective effect on the EAR and LAR. This is the first inhaled PDE4 inhibitor to show therapeutic potential in asthma.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00380354.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of the novel phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor MEM 1414 on the allergen induced responses in mild asthma.BMC Pulm Med. 2014 Oct 28;14:166. doi: 10.1186/1471-2466-14-166. BMC Pulm Med. 2014. PMID: 25351474 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and tolerability of the inhaled phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor GSK256066 in moderate COPD.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Oct;26(5):588-95. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2013.05.004. Epub 2013 May 21. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23701917 Clinical Trial.
-
In vivo characterization of GSK256066, a high-affinity inhaled phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Apr;337(1):137-44. doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.173641. Epub 2011 Jan 4. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21205924
-
Bimosiamose, an inhaled small-molecule pan-selectin antagonist, attenuates late asthmatic reactions following allergen challenge in mild asthmatics: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical cross-over-trial.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2006;19(4):233-41. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2005.07.004. Epub 2005 Sep 1. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16140027 Clinical Trial.
-
GSK256066, an exceptionally high-affinity and selective inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 4 suitable for administration by inhalation: in vitro, kinetic, and in vivo characterization.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Apr;337(1):145-54. doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.173690. Epub 2011 Jan 4. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21205923
Cited by
-
The reproducibility of bolus allergen challenges; power calculations for clinical trials.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 May;69(5):1187-8. doi: 10.1007/s00228-012-1442-z. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23128964 No abstract available.
-
An Overview of PDE4 Inhibitors in Clinical Trials: 2010 to Early 2022.Molecules. 2022 Aug 4;27(15):4964. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154964. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35956914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Effect of Leukotriene Biosynthesis Blockers and Inhibitors of Phosphodiesterase Enzyme in Patients with Bronchial Hyperreactivity.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018 Apr 23;6(5):777-781. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2018.187. eCollection 2018 May 20. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 29875845 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacology of novel treatments for COPD: are fixed dose combination LABA/LAMA synergistic?Eur Clin Respir J. 2015 Mar 16;2. doi: 10.3402/ecrj.v2.26634. eCollection 2015. Eur Clin Respir J. 2015. PMID: 26557255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human adipose tissue mesenchymal stromal cells and their extracellular vesicles act differentially on lung mechanics and inflammation in experimental allergic asthma.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Jun 24;8(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0600-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28646903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. http://www.ginasthma.com Last updated 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

