Regulation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptor expression in the rat striatum and prefrontal cortex in response to amphetamine in vivo
- PMID: 20193665
- PMCID: PMC2849858
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.02.062
Regulation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptor expression in the rat striatum and prefrontal cortex in response to amphetamine in vivo
Abstract
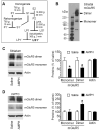
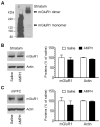
G protein-coupled metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) are expressed in widespread regions of the mammalian brain and are involved in the regulation of a variety of neuronal and synaptic activities. Group I mGluRs (mGluR1 and mGluR5 subtypes) are expressed in striatal medium spiny output neurons and are believed to play an important role in the modulation of cellular responses to dopamine stimulation with psychostimulants. In this study, we investigated the effect of a single dose of the psychostimulant amphetamine on mGluR1/5 protein expression in the rat forebrain in vivo. We found that acute systemic injection of amphetamine at a behaviorally active dose (5 mg/kg) was able to reduce mGluR5 protein levels in a confined biochemical fraction of synaptosomal plasma membranes enriched from the striatum. In contrast to the striatum, amphetamine increased mGluR5 protein levels in the medial prefrontal cortex. These changes in mGluR5 expression in both the striatum and the medial prefrontal cortex were transient and reversible. In addition, protein levels of mGluR1 in the enriched synaptosomal fraction from both the striatum and the medial prefrontal cortex remained stable in response to acute amphetamine. Similarly, Homer1b/c proteins, which are prominent anchoring proteins of mGluR1/5 and are highly expressed in the striatum and the medial prefrontal cortex, showed no change in their protein abundance in striatal and cortical synaptosomes after amphetamine administration. These data demonstrate differential sensitivity of mGluR1 and mGluR5 expression to amphetamine. Acute amphetamine injection is able to alter mGluR5 protein levels at synaptic sites in a subtype- and region-specific manner.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
mGluR5-dependent increases in immediate early gene expression in the rat striatum following acute administration of amphetamine.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004 Mar 30;122(2):151-7. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2003.12.010. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15010207
-
Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor mediates upregulation of transcription factor mRNA expression in rat striatum induced by acute administration of amphetamine.Brain Res. 2002 Jan 11;924(2):167-75. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(01)03230-9. Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 11750902
-
RGS4 overexpression in the rat dorsal striatum modulates mGluR5- and amphetamine-mediated behavior and signaling.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012 Jun;221(4):621-35. doi: 10.1007/s00213-011-2606-8. Epub 2011 Dec 23. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22193724 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of psychostimulant-induced signaling and gene expression in the striatum.J Neurochem. 2008 Mar;104(6):1440-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05240.x. Epub 2008 Jan 21. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 18221378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR1/5) in vitro and in vivo.Neuropharmacology. 2008 Sep;55(4):403-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.05.034. Epub 2008 Jun 10. Neuropharmacology. 2008. PMID: 18585398 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polyclonal antibodies selectively inhibit tumor growth and invasion and synergize with immune checkpoint inhibitors.JCI Insight. 2024 Feb 8;9(3):e166231. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.166231. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 38085594 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of Group I mGluRs and BDNF Associated with Behavioral Abnormity in Prenatally Stressed Offspring Rats.Neurochem Res. 2015 May;40(5):1074-82. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1565-6. Epub 2015 Apr 18. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 25894678
-
Synaptic ERK2 Phosphorylates and Regulates Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 1 In Vitro and in Neurons.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Nov;54(9):7156-7170. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0225-4. Epub 2016 Oct 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27796752 Free PMC article.
-
Stress hormone exposure reduces mGluR5 expression in the nucleus accumbens: functional implications for interoceptive sensitivity to alcohol.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014 Sep;39(10):2376-86. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.85. Epub 2014 Apr 9. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24713611 Free PMC article.
-
Hypersensitivity to amphetamine's psychomotor and reinforcing effects in serotonin transporter knockout rats: Glutamate in the nucleus accumbens.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 Oct;177(19):4532-4547. doi: 10.1111/bph.15211. Epub 2020 Aug 30. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32721055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ango F, Robbe D, Tu JC, Xiao B, Worley PF, Pin JP, Bockaert J, Fagni L. Homer-dependent cell surface expression of metabotropic glutamate receptor type 5 in neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2002;20:323–329. - PubMed
-
- Ary AW, Szumlinski KK. Regional differences in the effects of withdrawal from repeated cocaine upon Homer and glutamate receptor expression: a two-species comparison. Brain Res. 2007;1184:295–305. - PubMed
-
- Berke JD, Hyman SE. Addiction, dopamine, and the molecular mechanisms of memory. Neuron. 2000;25:515–532. - PubMed
-
- Brakeman PR, Lanahan AA, O’Brien R, Roche K, Barnes CA, Huganir RL, Worley PF. Homer: a protein that selectively binds metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nature. 1997;386:284–288. - PubMed
-
- Butcher SP, Fairbrother IS, Kelly JS, Arbuthnott GW. Amphetamine-induced dopamine release in the rat striatum: an in vivo microdialysis study. J Neurochem. 1988;50:346–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

