Identification of a structural element of the hepatitis C virus minus strand RNA involved in the initiation of RNA synthesis
- PMID: 20194114
- PMCID: PMC2896513
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq109
Identification of a structural element of the hepatitis C virus minus strand RNA involved in the initiation of RNA synthesis
Abstract
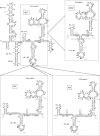
The replication of the genomic RNA of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) of positive polarity involves the synthesis of a replication intermediate of negative polarity by the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (NS5B). In vitro and likely in vivo, the NS5B initiates RNA synthesis without primers. This de novo mechanism needs specific interactions between the polymerase and viral RNA elements. Cis-acting elements involved in the initiation of (-) RNA synthesis have been identified in the 3' non-coding region and in the NS5B coding region of the HCV RNA. However, the detailed contribution of sequences and/or structures of (-) RNA involved in the initiation of (+) RNA synthesis has been less studied. In this report, we identified an RNA element localized between nucleotides 177 and 222 from the 3'-end of the (-) RNA that is necessary for efficient initiation of RNA synthesis by the recombinant NS5B. By site-directed mutagenesis experiments, we demonstrate that the structure rather than the primary sequence of this domain is important for RNA synthesis. We also demonstrate that the intact structure of this RNA element is also needed for efficient RNA synthesis when the viral NS5B functions in association with other viral and cellular proteins in cultured hepatic cells.
Figures
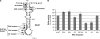

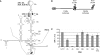

Similar articles
-
Template requirement and initiation site selection by hepatitis C virus polymerase on a minimal viral RNA template.J Biol Chem. 2000 Jun 9;275(23):17710-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M908781199. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10749880
-
Template requirements and binding of hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase during in vitro RNA synthesis from the 3'-end of virus minus-strand RNA.FEBS J. 2005 Aug;272(15):3872-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04804.x. FEBS J. 2005. PMID: 16045758
-
HCV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase replicates in vitro the 3' terminal region of the minus-strand viral RNA more efficiently than the 3' terminal region of the plus RNA.Eur J Biochem. 2001 Nov;268(22):5857-67. doi: 10.1046/j.0014-2956.2001.02532.x. Eur J Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11722573
-
Template requirements for de novo RNA synthesis by hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5B polymerase on the viral X RNA.J Virol. 2002 Jul;76(14):6944-56. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.14.6944-6956.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12072495 Free PMC article.
-
[Structure and function of the non-coding regions of hepatitis C viral RNA].Postepy Biochem. 2006;52(1):62-71. Postepy Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16869303 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
cis-Acting RNA elements in the hepatitis C virus RNA genome.Virus Res. 2015 Aug 3;206:90-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2014.12.029. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Virus Res. 2015. PMID: 25576644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signals Involved in Regulation of Hepatitis C Virus RNA Genome Translation and Replication.Front Microbiol. 2018 Mar 12;9:395. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00395. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29593672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutations of the SL2 dimerization sequence of the hepatitis C genome abrogate viral replication.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Sep;72(17):3375-85. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1893-3. Epub 2015 Mar 28. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25822205 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C Virus Replication.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2020 Mar 2;10(3):a037093. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a037093. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2020. PMID: 31570388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conserved RNA secondary structures and long-range interactions in hepatitis C viruses.RNA. 2015 Jul;21(7):1219-32. doi: 10.1261/rna.049338.114. Epub 2015 May 11. RNA. 2015. PMID: 25964384 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choo QL, Kuo G, Weiner AJ, Overby LR, Bradley DW, Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989;244:359–362. - PubMed
-
- Penin F, Dubuisson J, Rey FA, Moradpour D, Pawlotsky JM. Structural biology of hepatitis C virus. Hepatology. 2004;39:5–19. - PubMed
-
- Honda M, Ping LH, Rijnbrand RC, Amphlett E, Clarke B, Rowlands D, Lemon SM. Structural requirements for initiation of translation by internal ribosome entry within genome-length hepatitis C virus RNA. Virology. 1996;222:31–42. - PubMed
-
- Moriishi K, Matsuura Y. Host factors involved in the replication of hepatitis C virus. Rev. Med. Virol. 2007;17:343–354. - PubMed

