Multiple markers of inflammation and weight status: cross-sectional analyses throughout childhood
- PMID: 20194272
- PMCID: PMC2909480
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2009-2182
Multiple markers of inflammation and weight status: cross-sectional analyses throughout childhood
Abstract
Objective: Inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) are related to obesity in adults, but the association is less clear in children. Our objective was to examine relationships between multiple markers of inflammation and children's weight status; we hypothesized that the prevalence of inflammatory markers would increase as weight status increased.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of children in the United States aged 1 to 17 years in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999-2006. Children were categorized using weight-for-length when age <2 years and BMI for > or =2 years, as very obese (> or =99th percentile), obese (<99th and > or =95th percentile), overweight (<95th and > or =85th percentile), and healthy weight (>5th to < or =85th percentile) according to expert consensus. Our main outcome measures were high-sensitivity CRP and absolute neutrophil count, in addition to a novel third measure: ferritin controlled for iron status using a ferritin/transferrin ratio. We used Cox proportional hazards models to examine risk of abnormal values of inflammatory markers according to weight.
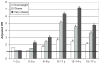
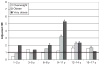
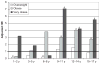
Results: Increased risk of a CRP level of >1.0 mg/L was evident among very obese children from ages 3 to 5 years (hazard ratio [HR]: 2.29; P < .01) through 15 to 17 years (HR: 4.73; P < .01). Increased risk of abnormal neutrophil count among very obese children began at 6 to 8 years (HR: 2.00; P = .049), and increased prevalence of abnormal ferritin/transferrin ratio began at 9 to 11 years (HR: 7.06; P < .001).
Conclusions: Multiple inflammatory markers are strongly and positively associated with increasing weight status in children, and this relationship starts as young as age 3. Elevated inflammatory markers in very young obese children are particularly concerning, because inflammation may cause long-term, cumulative vascular damage. This deserves additional research via longitudinal design.
Figures
References
-
- Poirier P, Giles TD, Bray GA, et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: pathophysiology, evaluation, and effect of weight loss. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26(5):968–976. - PubMed
-
- Visser M, Bouter LM, McQuillan GM, Wener MH, Harris TB. Elevated C-reactive protein levels in overweight and obese adults. JAMA. 1999;282(22):2131–2135. - PubMed
-
- Fogarty AW, Glancy C, Jones S, Lewis SA, McKeever TM, Britton JR. A prospective study of weight change and systemic inflammation over 9 y. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87(1):30–35. - PubMed
-
- Selvin E, Paynter NP, Erlinger TP. The effect of weight loss on C-reactive protein: a systematic review. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167(1):31–39. - PubMed
-
- Das UN. Is obesity an inflammatory condition? Nutrition. 2001;17(11–12):953–966. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

