KDM7 is a dual demethylase for histone H3 Lys 9 and Lys 27 and functions in brain development
- PMID: 20194436
- PMCID: PMC2827838
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1864410
KDM7 is a dual demethylase for histone H3 Lys 9 and Lys 27 and functions in brain development
Abstract
Methylation of histone H3 Lys 9 and Lys 27 (H3K9 and H3K27) is associated with transcriptional silencing. Here we show that KDM7, a JmjC domain-containing protein, catalyzes demethylation of both mono- or dimethylated H3K9 and H3K27. Inhibition of KDM7 orthologs in zebrafish resulted in developmental brain defects. KDM7 interacts with the follistatin gene locus, and KDM7 depletion in mammalian neuronal cells suppressed follistatin gene transcription in association with increased levels of dimethylated H3K9 and H3K27. Our findings identify KDM7 as a dual demethylase for H3K9 and H3K27 that functions as an eraser of silencing marks on chromatin during brain development.
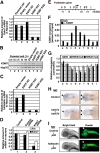
Figures



References
-
- Allis CD, Berger SL, Cote J, Dent S, Jenuwien T, Kouzarides T, Pillus L, Reinberg D, Shi Y, Shiekhattar R, et al. New nomenclature for chromatin-modifying enzymes. Cell. 2007;131:633–636. - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Schneider R, Kouzarides T. Histone methylation: Dynamic or static? Cell. 2002;109:801–806. - PubMed
-
- Hasenpusch-Theil K, Chadwick BP, Theil T, Heath SK, Wilkinson DG, Frischauf AM. PHF2, a novel PHD finger gene located on human chromosome 9q22. Mamm Genome. 1999;10:294–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
