Bifrontal, bitemporal and right unilateral electrode placement in ECT: randomised trial
- PMID: 20194546
- PMCID: PMC2830057
- DOI: 10.1192/bjp.bp.109.066183
Bifrontal, bitemporal and right unilateral electrode placement in ECT: randomised trial
Abstract
Background: Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is an effective treatment for major depression. Optimising efficacy and minimising cognitive impairment are goals of ongoing technical refinements.
Aims: To compare the efficacy and cognitive effects of a novel electrode placement, bifrontal, with two standard electrode placements, bitemporal and right unilateral in ECT.
Method: This multicentre randomised, double-blind, controlled trial (NCT00069407) was carried out from 2001 to 2006. A total of 230 individuals with major depression, bipolar and unipolar, were randomly assigned to one of three electrode placements during a course of ECT: bifrontal at one and a half times seizure threshold, bitemporal at one and a half times seizure threshold and right unilateral at six times seizure threshold.
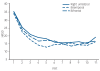
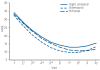
Results: All three electrode placements resulted in both clinically and statistically significant antidepressant outcomes. Remission rates were 55% (95% CI 43-66%) with right unilateral, 61% with bifrontal (95% CI 50-71%) and 64% (95% CI 53-75%) with bitemporal. Bitemporal resulted in a more rapid decline in symptom ratings over the early course of treatment. Cognitive data revealed few differences between the electrode placements on a variety of neuropsychological instruments.
Conclusions: Each electrode placement is a very effective antidepressant treatment when given with appropriate electrical dosing. Bitemporal leads to more rapid symptom reduction and should be considered the preferred placement for urgent clinical situations. The cognitive profile of bifrontal is not substantially different from that of bitemporal.
Figures

Comment in
-
Electroconvulsive therapy, practice and evidence.Br J Psychiatry. 2010 Mar;196(3):171-2. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.109.074054. Br J Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 20194535
-
Bifrontal, bitemporal and right unilateral ECT electrode placement are similarly effective for reducing depressive symptoms.Evid Based Ment Health. 2010 Aug;13(3):85. doi: 10.1136/ebmh.13.3.85. Evid Based Ment Health. 2010. PMID: 20682825 No abstract available.
References
-
- Friedman E. Unidirectional electrostimulated convulsive therapy. I: The effect of wave form and stimulus characteristics on the convulsive dose. Am J Psychiatry 1942; 99: 218–23.
-
- Lancaster neuropsychological, Steinert RR, Frost I. Unilateral electroconvulsive therapy. J Ment Sci 1958; 104: 221–7. - PubMed
-
- Fink M. Convulsive Therapy: Theory and Practice. Raven Press Books, 1979.
-
- D’Elia G, Frederiksen SO, Raotma H, Widepalm K. Comparison of fronto-frontal and temporo-parietal unilateral ECT. Acta Psychiatr Scand 1977; 56: 233–9. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Task Force on Electroconvulsive Therapy. The Practice of Electroconvulsive Therapy: Recommendations for Treatment, Training, and Privileging. APA, 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

