CCR7-dependent immunity during acute Toxoplasma gondii infection
- PMID: 20194594
- PMCID: PMC2863519
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01314-09
CCR7-dependent immunity during acute Toxoplasma gondii infection
Abstract
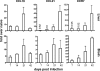
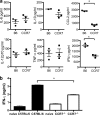
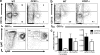
The chemokine receptor CCR7 is a well-established homing receptor for dendritic cells and T cells. Interactions with its ligands, CCL19 and CCL21, facilitate priming of immune responses in lymphoid tissue, yet CCR7-independent immune responses can be generated in the presence of sufficient antigen. In these studies, we investigated the role of CCR7 signaling in the generation of protective immune responses to the intracellular protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. The results demonstrated a significant increase in the expression of CCL19, CCL21, and CCR7 in peripheral and central nervous system (CNS) tissues over the course of infection. Unexpectedly, despite the presence of abundant antigen, CCR7 was an absolute requirement for protective immunity to T. gondii, as CCR7(-/-) mice succumbed to the parasite early in the acute phase of infection. Although serum levels of interleukin 12 (IL-12), IL-6, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), and IL-10 remained unchanged, there was a significant decrease in CCL2/monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) and inflammatory monocyte recruitment to the site of infection. In addition, CCR7(-/-) mice failed to produce sufficient gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), a critical Th1-associated effector cytokine required to control parasite replication. As a result, there was increased parasite dissemination and a significant increase in parasite burden in the lungs, livers, and brains of infected mice. Adoptive-transfer experiments revealed that expression of CCR7 on the T-cell compartment alone is sufficient to enable T-cell priming, increase IFN-gamma production, and allow the survival of CCR7(-/-) mice. These data demonstrate an absolute requirement for T-cell expression of CCR7 for the generation of protective immune responses to Toxoplasma infection.
Figures

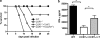
Similar articles
-
CCR7 deficiency leads to leukocyte activation and increased clearance in response to pulmonary Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection.Infect Immun. 2010 May;78(5):2099-107. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00962-09. Epub 2010 Feb 22. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20176793 Free PMC article.
-
[Rudolf-Virchow Prize 1998. Award lecture. Toxoplasmosis: a model infection for studying systemic and intracerebral immune reactions].Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 1998;82:9-22. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 1998. PMID: 10095413 German.
-
A myriad of functions and complex regulation of the CCR7/CCL19/CCL21 chemokine axis in the adaptive immune system.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Jun;24(3):269-83. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.03.001. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 23587803 Review.
-
Kinetics of systemic cytokine and brain chemokine gene expression in murine toxoplasma infection.J Parasitol. 2008 Dec;94(6):1282-8. doi: 10.1645/GE-1309.1. J Parasitol. 2008. PMID: 19127964
-
Cell-mediated immunity to Toxoplasma gondii: initiation, regulation and effector function.Immunobiology. 1999 Dec;201(2):240-7. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(99)80064-3. Immunobiology. 1999. PMID: 10631573 Review.
Cited by
-
Lymphoid chemokines in the CNS.J Neuroimmunol. 2010 Jul 27;224(1-2):56-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2010.05.017. Epub 2010 Jun 1. J Neuroimmunol. 2010. PMID: 20605642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The protective and pathogenic roles of CXCL17 in human health and disease: Potential in respiratory medicine.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020 Jun;53:53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.04.004. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020. PMID: 32345516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proinflammatory and regulatory cytokines and chemokines in infants with uncomplicated and severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria.Clin Exp Immunol. 2011 Nov;166(2):218-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04474.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21985368 Free PMC article.
-
Central Nervous System Stromal Cells Control Local CD8(+) T Cell Responses during Virus-Induced Neuroinflammation.Immunity. 2016 Mar 15;44(3):622-633. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.12.022. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Immunity. 2016. PMID: 26921107 Free PMC article.
-
Role of C-C chemokine receptor type 7 and its ligands during neuroinflammation.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Apr 25;9:77. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-77. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22533989 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aliberti, J., D. Jankovic, and A. Sher. 2004. Turning it on and off: regulation of dendritic cell function in Toxoplasma gondii infection. Immunol. Rev. 201:26-34. - PubMed
-
- Bajenoff, M., J. G. Egen, H. Qi, A. Y. Huang, F. Castellino, and R. N. Germain. 2007. Highways, byways and breadcrumbs: directing lymphocyte traffic in the lymph node. Trends Immunol. 28:346-352. - PubMed
-
- Bromley, S. K., T. R. Mempel, and A. D. Luster. 2008. Orchestrating the orchestrators: chemokines in control of T cell traffic. Nat. Immunol. 9:970-980. - PubMed
-
- Collazo, C. M., G. S. Yap, G. D. Sempowski, K. C. Lusby, L. Tessarollo, G. F. Woude, A. Sher, and G. A. Taylor. 2001. Inactivation of LRG-47 and IRG-47 reveals a family of interferon gamma-inducible genes with essential, pathogen-specific roles in resistance to infection. J. Exp. Med. 194:181-188. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

