Disruption of the Rickettsia rickettsii Sca2 autotransporter inhibits actin-based motility
- PMID: 20194597
- PMCID: PMC2863521
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00100-10
Disruption of the Rickettsia rickettsii Sca2 autotransporter inhibits actin-based motility
Abstract
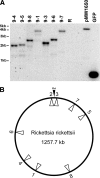
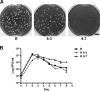
Rickettsii rickettsii, the etiologic agent of Rocky Mountain spotted fever, replicates within the cytosol of infected cells and uses actin-based motility to spread inter- and intracellularly. Although the ultrastructure of the actin tail and host proteins associated with it are distinct from those of Listeria or Shigella, comparatively little is known regarding the rickettsial proteins involved in its organization. Here, we have used random transposon mutagenesis of R. rickettsii to generate a small-plaque mutant that is defective in actin-based motility and does not spread directly from cell to cell as is characteristic of spotted fever group rickettsiae. The transposon insertion site of this mutant strain was within Sca2, a member of a family of large autotransporter proteins. Sca2 exhibits several features suggestive of its apparent role in actin-based motility. It displays an N-terminal secretory signal peptide, a C-terminal predicted autotransporter domain, up to four predicted Wasp homology 2 (WH2) domains, and two proline-rich domains, one with similarity to eukaryotic formins. In a guinea pig model of infection, the Sca2 mutant did not elicit fever, suggesting that Sca2 and actin-based motility are virulence factors of spotted fever group rickettsiae.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulator of Actin-Based Motility (RoaM) Downregulates Actin Tail Formation by Rickettsia rickettsii and Is Negatively Selected in Mammalian Cell Culture.mBio. 2022 Apr 26;13(2):e0035322. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00353-22. Epub 2022 Mar 14. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35285700 Free PMC article.
-
Proteolytic Cleavage of the Immunodominant Outer Membrane Protein rOmpA in Rickettsia rickettsii.J Bacteriol. 2017 Feb 28;199(6):e00826-16. doi: 10.1128/JB.00826-16. Print 2017 Mar 15. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 28031280 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic comparison of virulent Rickettsia rickettsii Sheila Smith and avirulent Rickettsia rickettsii Iowa.Infect Immun. 2008 Feb;76(2):542-50. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00952-07. Epub 2007 Nov 19. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18025092 Free PMC article.
-
Rocky Mountain spotted fever.Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1991 Mar;5(1):19-35. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1991. PMID: 1904897 Review.
-
Rocky Mountain spotted fever: a disease in need of microbiological concern.Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jul;2(3):227-40. doi: 10.1128/CMR.2.3.227. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989. PMID: 2504480 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative genome sequencing of Rickettsia rickettsii strains that differ in virulence.Infect Immun. 2015 Apr;83(4):1568-76. doi: 10.1128/IAI.03140-14. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 25644009 Free PMC article.
-
Rickettsia buchneri sp. nov., a rickettsial endosymbiont of the blacklegged tick Ixodes scapularis.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2015 Mar;65(Pt 3):965-970. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.000047. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25563918 Free PMC article.
-
Actin-based motility of bacterial pathogens: mechanistic diversity and its impact on virulence.Pathog Dis. 2016 Nov 1;74(8):ftw099. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftw099. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Pathog Dis. 2016. PMID: 27655913 Free PMC article.
-
Transformation frequency of a mariner-based transposon in Rickettsia rickettsii.J Bacteriol. 2011 Sep;193(18):4993-5. doi: 10.1128/JB.05279-11. Epub 2011 Jul 15. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21764933 Free PMC article.
-
Rickettsia actin-based motility occurs in distinct phases mediated by different actin nucleators.Curr Biol. 2014 Jan 6;24(1):98-103. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.11.025. Epub 2013 Dec 19. Curr Biol. 2014. PMID: 24361066 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

