Anthrax lethal toxin impairs CD1d-mediated antigen presentation by targeting the extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway
- PMID: 20194602
- PMCID: PMC2863516
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01307-09
Anthrax lethal toxin impairs CD1d-mediated antigen presentation by targeting the extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway
Abstract
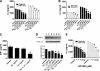
Lethal toxin (LT) is a critical virulence factor of Bacillus anthracis and an important means by which this bacterium evades the host's immune system. In this study, we demonstrate that CD1d-expressing cells treated with LT have reduced CD1d-mediated antigen presentation. We earlier showed an important role for the mitogen-activated protein kinase extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) in the regulation of CD1d-mediated antigen presentation, and we report here that LT impairs antigen presentation by CD1d in an ERK1/2-dependent manner. Similarly, LT and the ERK1/2 pathway-specific inhibitor U0126 caused a decrease in major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II-mediated antigen presentation. Confocal microscopy analyses revealed altered intracellular distribution of CD1d and LAMP-1 in LT-treated cells, similar to the case for ERK1/2-inhibited cells. These results suggest that Bacillus anthracis has the ability to evade the host's innate immune system by reducing CD1d-mediated antigen presentation through targeting the ERK1/2 pathway.
Figures
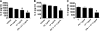
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of CD1d-mediated antigen presentation by the transforming growth factor-β/Smad signalling pathway.Immunology. 2014 Dec;143(4):679-91. doi: 10.1111/imm.12353. Immunology. 2014. PMID: 24990409 Free PMC article.
-
CD1d-dependent B-cell help by NK-like T cells leads to enhanced and sustained production of Bacillus anthracis lethal toxin-neutralizing antibodies.Infect Immun. 2010 Apr;78(4):1610-7. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00002-10. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20123711 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus anthracis lethal toxin disrupts TCR signaling in CD1d-restricted NKT cells leading to functional anergy.PLoS Pathog. 2009 Sep;5(9):e1000588. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000588. Epub 2009 Sep 25. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19779559 Free PMC article.
-
Anthrax toxins: A paradigm of bacterial immune suppression.Trends Immunol. 2006 Sep;27(9):434-40. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2006.07.002. Epub 2006 Jul 24. Trends Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16861036 Review.
-
CD1 antigen presentation and infectious disease.Contrib Microbiol. 2003;10:164-82. doi: 10.1159/000068136. Contrib Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12530326 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune-Stimulatory and Therapeutic Activity of Tinospora cordifolia: Double-Edged Sword against Salmonellosis.J Immunol Res. 2017;2017:1787803. doi: 10.1155/2017/1787803. Epub 2017 Nov 26. J Immunol Res. 2017. PMID: 29318160 Free PMC article.
-
AB toxins: a paradigm switch from deadly to desirable.Toxins (Basel). 2010 Jul;2(7):1612-45. doi: 10.3390/toxins2071612. Epub 2010 Jun 25. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22069653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anthrax lethal toxin and the induction of CD4 T cell immunity.Toxins (Basel). 2012 Oct;4(10):878-99. doi: 10.3390/toxins4100878. Epub 2012 Oct 19. Toxins (Basel). 2012. PMID: 23162703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anthrax lethal factor as an immune target in humans and transgenic mice and the impact of HLA polymorphism on CD4+ T cell immunity.PLoS Pathog. 2014 May 1;10(5):e1004085. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004085. eCollection 2014 May. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24788397 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of CD1d-mediated antigen presentation by the transforming growth factor-β/Smad signalling pathway.Immunology. 2014 Dec;143(4):679-91. doi: 10.1111/imm.12353. Immunology. 2014. PMID: 24990409 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

