Expansion and evolution of the Streptococcus pneumoniae Spain9V-ST156 clonal complex in Poland
- PMID: 20194703
- PMCID: PMC2863602
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01340-09
Expansion and evolution of the Streptococcus pneumoniae Spain9V-ST156 clonal complex in Poland
Abstract
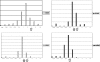
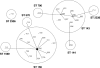
In this study, we analyzed 118 penicillin-nonsusceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae (PNSP) isolates (MICs, >or=0.12 microg/ml) recovered in Poland in 2003 to 2005 from patients with respiratory tract diseases and invasive infections. Seven different serotypes (14, 9V, 23F, 19F, 6B, 19A, and 6A, in order of descending frequency), seven alleles of the murM gene (murMA, murMB6, and the new murMB12 to -16 alleles), and 31 multilocus sequence types (STs) were observed. The vast majority of the PNSP isolates (90.7%) belonged to the international multiresistant clones, and among these, the Spain(9V)-ST156 clonal complex was the most prevalent (56 isolates) and was significantly overrepresented in invasive infections. The clone has been evolving rapidly, as demonstrated by the observed number of STs, the diversity in multiple-locus variable-number-tandem-repeat analysis (MLVA) types, and the polymorphism of pbp and pspA genes (coding for penicillin-binding proteins and the pneumococcal surface protein A, respectively). The presence and structure of the rlrA islet (encoding the pneumococcal pilus) were very well conserved. The Spain(9V)-ST156 clonal complex has been largely responsible for a decreasing susceptibility to penicillin among pneumococci in Poland in recent years, in spite of a relatively moderate antimicrobial use.
Figures

References
-
- Albarracín Orio, A. G., P. R. Cortes, M. Tregnaghi, G. E. Piñas, Argentinean Network Pneumococcus Study Group, and J. R. Echenique. 2008. A new serotype 14 variant of the pneumococcal Spain9V-3 international clone detected in the central region of Argentina. J. Med. Microbiol. 57:992-999. - PubMed
-
- Austrian, R. 1981. Pneumococcus: the first one hundred years. Rev. Infect. Dis. 3:183-189. - PubMed
-
- Barocchi, M. A., J. Ries, X. Zogaj, C. Hemsley, B. Albiger, A. Kanth, S. Dahlberg, J. Fernebro, M. Moschioni, V. Masignani, K. Hultenby, A. R. Taddei, K. Beiter, F. Wartha, A. von Euler, A. Covacci, D. W. Holden, S. Normark, R. Rappuoli, and B. Henriques-Normark. 2006. A pneumococcal pilus influences virulence and host inflammatory responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103:2857-2862. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

