MicroRNAs add a new dimension to cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 20194875
- PMCID: PMC2847432
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.889048
MicroRNAs add a new dimension to cardiovascular disease
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
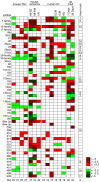
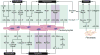
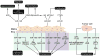
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. - PubMed
-
- Denli AM, Tops BB, Plasterk RH, Ketting RF, Hannon GJ. Processing of primary microRNAs by the Microprocessor complex. Nature. 2004;432:231–235. - PubMed
-
- Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ, Parker R. Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Genes Dev. 2006;20:515–524. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

