Increasing the efficacy of CD20 antibody therapy through the engineering of a new type II anti-CD20 antibody with enhanced direct and immune effector cell-mediated B-cell cytotoxicity
- PMID: 20194898
- PMCID: PMC2881503
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-06-225979
Increasing the efficacy of CD20 antibody therapy through the engineering of a new type II anti-CD20 antibody with enhanced direct and immune effector cell-mediated B-cell cytotoxicity
Abstract
CD20 is an important target for the treatment of B-cell malignancies, including non-Hodgkin lymphoma as well as autoimmune disorders. B-cell depletion therapy using monoclonal antibodies against CD20, such as rituximab, has revolutionized the treatment of these disorders, greatly improving overall survival in patients. Here, we report the development of GA101 as the first Fc-engineered, type II humanized IgG1 antibody against CD20. Relative to rituximab, GA101 has increased direct and immune effector cell-mediated cytotoxicity and exhibits superior activity in cellular assays and whole blood B-cell depletion assays. In human lymphoma xenograft models, GA101 exhibits superior antitumor activity, resulting in the induction of complete tumor remission and increased overall survival. In nonhuman primates, GA101 demonstrates superior B cell-depleting activity in lymphoid tissue, including in lymph nodes and spleen. Taken together, these results provide compelling evidence for the development of GA101 as a promising new therapy for the treatment of B-cell disorders.
Figures

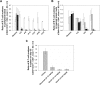
 ) was compared with rituximab (2 × 10 mg/kg,
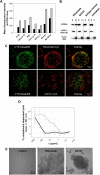
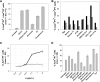
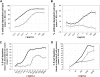
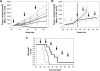
) was compared with rituximab (2 × 10 mg/kg,  ) and vehicle (□) after 2 intravenous doses administered on days 0 and 7 to male and female cynomolgus monkeys (n = 3 per group; 1 female, 2 males). Peripheral blood and lymph node B-cell numbers were evaluated at baseline (day −7) and on the indicated days by flow cytometric analysis. B-cell numbers were evaluated in the spleens of the treated animals on day 35. (A) Mean B-cell numbers expressed as B-/T-cell ratios in peripheral blood of cynomolgus monkeys treated with GA101 and rituximab. (B) Mean B-cell numbers expressed as B-/T-cell ratios in the lymph nodes of cynomolgus monkeys treated with GA101 and rituximab. (C) Mean B-cell numbers expressed as B-/T-cell ratios in the spleens of cynomolgus monkeys treated with GA101 and rituximab on day 35. GA101 treatment resulted in statistically superior depletion of total B cells from lymph nodes, compared with rituximab, from days 9 to 35, with a decrease in B-cell numbers of more than 95%. Data are mean ± SD.
) and vehicle (□) after 2 intravenous doses administered on days 0 and 7 to male and female cynomolgus monkeys (n = 3 per group; 1 female, 2 males). Peripheral blood and lymph node B-cell numbers were evaluated at baseline (day −7) and on the indicated days by flow cytometric analysis. B-cell numbers were evaluated in the spleens of the treated animals on day 35. (A) Mean B-cell numbers expressed as B-/T-cell ratios in peripheral blood of cynomolgus monkeys treated with GA101 and rituximab. (B) Mean B-cell numbers expressed as B-/T-cell ratios in the lymph nodes of cynomolgus monkeys treated with GA101 and rituximab. (C) Mean B-cell numbers expressed as B-/T-cell ratios in the spleens of cynomolgus monkeys treated with GA101 and rituximab on day 35. GA101 treatment resulted in statistically superior depletion of total B cells from lymph nodes, compared with rituximab, from days 9 to 35, with a decrease in B-cell numbers of more than 95%. Data are mean ± SD.Comment in
-
Possible misinterpretation of the mode of action of therapeutic antibodies in vitro: homotypic adhesion and flow cytometry result in artefactual direct cell death.Blood. 2010 Oct 28;116(17):3372-3; author reply 3373-4. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-289736. Blood. 2010. PMID: 21030571 No abstract available.
References
-
- Tilly H, Zelenetz A. Treatment of follicular lymphoma: current status. Leuk Lymphoma. 2008;49(suppl 1):7–17. - PubMed
-
- Cvetković RS, Perry CM. Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Drugs. 2006;66(6):791–820. - PubMed
-
- Gürcan HM, Keskin DB, Stern JN, Nitzberg MA, Shekhani H, Ahmed AR. A review of the current use of rituximab in autoimmune diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 2009;9(1):10–25. - PubMed
-
- Cartron G, Watier H, Golay J, Solal-Celigny P. From the bench to the bedside: ways to improve rituximab efficacy. Blood. 2004;104(9):2635–2642. - PubMed
-
- Glennie MJ, French RR, Cragg MS, Taylor RP. Mechanisms of killing by anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies. Mol Immunol. 2007;44(16):3823–3837. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

