Molecular blockade of VEGFR2 in human epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells
- PMID: 20195243
- PMCID: PMC2878326
- DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.52
Molecular blockade of VEGFR2 in human epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells
Abstract
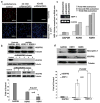
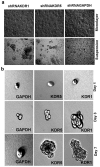
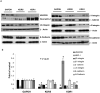
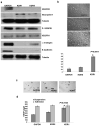
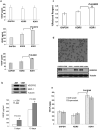
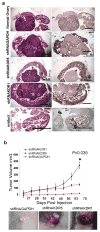
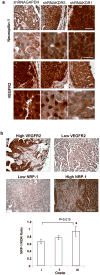
Human epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) is the most lethal neoplasm affecting the female genital tract, and is characterized by overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and growth as ascites. Anti-VEGF strategies are currently used in EOC therapy with promising results; however, molecular targeting of specific VEGF receptors on the cancer cells themselves has not been explored to date. We previously showed that activation of a VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling loop in EOC cells supports their survival in suspension, and short-term pharmacological inhibition of this loop increased EOC cell apoptosis in vitro. In this study, we stably knocked down VEGFR2 in OVCAR-3 and SKOV-3 EOC cells using short hairpin RNA (shRNA), an RNA interference strategy that could potentially overcome chemoresistance arising with angiogenic inhibitors. Unexpectedly, we observed an induction of more aggressive cellular behavior in transfected cells, leading to increased growth in mouse xenografts, enhanced accumulation of ascites, increased VEGF and neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) expression, and decreased expression of adhesion proteins, notably cadherins and integrins. Sonic hedgehog (SHH) pathways do not seem to be involved in the upregulation of NRP-1 message in VEGFR2 knockdown cells. Supporting our mouse model, we also found a significant increase in the ratio between NRP-1 and VEGFR2 with increasing tumor grade in 80 cases of human EOC. The change in EOC behavior that we report in this study occurred independent of the angiogenic response and shows the direct effect of VEGF blockade on the cancer cells themselves. Our findings highlight the possible confounding events that may affect the usefulness of RNAi in a therapeutic setting for disrupting EOC cell survival in ascites.
Figures

References
-
- Dinulescu DM, Ince TA, Quade BJ, et al. Role of K-ras and pten in the development of mouse models of endometriosis and endometrioid ovarian cancer. Nat Med. 2005;11:63–70. - PubMed
-
- Look M, Chang D, Sugarbaker PH, et al. Long-term results of cytoreductive surgery for advanced and recurrent epithelial ovarian cancers and papillary serous carcinoma of the peritoneum. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2003;13:764–770. - PubMed
-
- Wey JS, Stoeltzing O, Ellis LM, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptors: Expression and function in solid tumors. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2004;2:37–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

