Differentiation, distribution and gammadelta T cell-driven regulation of IL-22-producing T cells in tuberculosis
- PMID: 20195465
- PMCID: PMC2829073
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000789
Differentiation, distribution and gammadelta T cell-driven regulation of IL-22-producing T cells in tuberculosis
Abstract
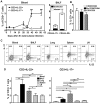
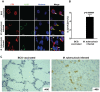
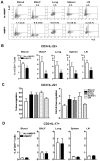
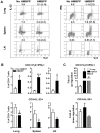
Differentiation, distribution and immune regulation of human IL-22-producing T cells in infections remain unknown. Here, we demonstrated in a nonhuman primate model that M. tuberculosis infection resulted in apparent increases in numbers of T cells capable of producing IL-22 de novo without in vitro Ag stimulation, and drove distribution of these cells more dramatically in lungs than in blood and lymphoid tissues. Consistently, IL-22-producing T cells were visualized in situ in lung tuberculosis (TB) granulomas by confocal microscopy and immunohistochemistry, indicating that mature IL-22-producing T cells were present in TB granuloma. Surprisingly, phosphoantigen HMBPP activation of Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells down-regulated the capability of T cells to produce IL-22 de novo in lymphocytes from blood, lung/BAL fluid, spleen and lymph node. Up-regulation of IFNgamma-producing Vgamma2Vdelta2 T effector cells after HMBPP stimulation coincided with the down-regulated capacity of these T cells to produce IL-22 de novo. Importantly, anti-IFNgamma neutralizing Ab treatment reversed the HMBPP-mediated down-regulation effect on IL-22-producing T cells, suggesting that Vgamma2Vdelta2 T-cell-driven IFNgamma-networking function was the mechanism underlying the HMBPP-mediated down-regulation of the capability of T cells to produce IL-22. These novel findings raise the possibility to ultimately investigate the function of IL-22 producing T cells and to target Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells for balancing potentially hyper-activating IL-22-producing T cells in severe TB.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Wolk K, Sabat R. Interleukin-22: a novel T- and NK-cell derived cytokine that regulates the biology of tissue cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006;17:367–380. - PubMed
-
- Wolk K, Kunz S, Witte E, Friedrich M, Asadullah K, et al. IL-22 increases the innate immunity of tissues. Immunity. 2004;21:241–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

