Helper T cell epitope-mapping reveals MHC-peptide binding affinities that correlate with T helper cell responses to pneumococcal surface protein A
- PMID: 20195541
- PMCID: PMC2828482
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009432
Helper T cell epitope-mapping reveals MHC-peptide binding affinities that correlate with T helper cell responses to pneumococcal surface protein A
Abstract
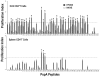
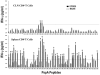
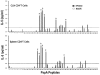
Understanding the requirements for protection against pneumococcal carriage and pneumonia will greatly benefit efforts in controlling these diseases. Several proteins and polysaccharide capsule have recently been implicated in the virulence of and protective immunity against Streptococcus pneumonia. Pneumococcal surface protein A (PspA) is highly conserved among S. pneumonia strains, inhibits complement activation, binds lactoferrin, elicits protective systemic immunity against pneumococcal infection, and is necessary for full pneumococcal virulence. Identification of PspA peptides that optimally bind human leukocyte antigen (HLA) would greatly contribute to global vaccine efforts, but this is hindered by the multitude of HLA polymorphisms. Here, we have used an experimental data set of 54 PspA peptides and in silico methods to predict peptide binding to HLA and murine major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II. We also characterized spleen- and cervical lymph node (CLN)-derived helper T lymphocyte (HTL) cytokine responses to these peptides after S. pneumonia strain EF3030-challenge in mice. Individual, yet overlapping peptides, 15 amino acids in length revealed residues 199 to 246 of PspA (PspA(199-246)) consistently caused the greatest IFN-gamma, IL-2, IL-5 and proliferation as well as moderate IL-10 and IL-4 responses by ex vivo stimulated splenic and CLN CD4(+) T cells isolated from S. pneumonia strain EF3030-challeged F(1) (B6xBALB/c) mice. IEDB, RANKPEP, SVMHC, MHCPred, and SYFPEITHI in silico analysis tools revealed peptides in PspA(199-246) also interact with a broad range of HLA-DR, -DQ, and -DP allelles. These data suggest that predicted MHC class II-peptide binding affinities do not always correlate with T helper (Th) cytokine or proliferative responses to PspA peptides, but when used together with in vivo validation can be a useful tool to choose candidate pneumococcal HTL epitopes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Nasrin D, Collignon PJ, Wilson EJ, Pilotto LS, Douglas RM. Antibiotic resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae isolated from children. Journal of Paediatrics & Child Health. 1999;35:558–561. - PubMed
-
- Morita JY, Zell ER, Danila R, Farley MM, Hadler J, et al. Association between antimicrobial resistance among pneumococcal isolates and burden of invasive pneumococcal disease in the community. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2002;35:420–427. - PubMed
-
- Richter SS, Heilmann KP, Coffman SL, Huynh HK, Brueggemann AB, et al. The molecular epidemiology of penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae in the United States, 1994–2000. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2002;34:330–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

