miR-24 regulates apoptosis by targeting the open reading frame (ORF) region of FAF1 in cancer cells
- PMID: 20195546
- PMCID: PMC2828487
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009429
miR-24 regulates apoptosis by targeting the open reading frame (ORF) region of FAF1 in cancer cells
Abstract
Background: microRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs that regulate cognate mRNAs at the post-transcriptional stage. Several studies have shown that miRNAs modulate gene expression in mammalian cells by base pairing to complementary sites in the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of the target mRNAs.
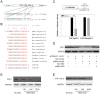
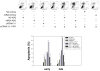
Methodology/principal findings: In the present study, miR-24 was found to target fas associated factor 1(FAF1) by binding to its amino acid coding sequence (CDS) region, thereby regulating apoptosis in DU-145 cells. This result supports an augmented model whereby animal miRNAs can exercise their effects through binding to the CDS region of the target mRNA. Transfection of miR-24 antisense oligonucleotide (miR-24-ASO) also induced apoptosis in HGC-27, MGC-803 and HeLa cells.
Conclusions/significance: We found that miR-24 regulates apoptosis by targeting FAF1 in cancer cells. These findings suggest that miR-24 could be an effective drug target for treatment of hormone-insensitive prostate cancer or other types of cancers. Future work may further develop miR-24 for therapeutic applications in cancer biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
miR-181b promotes cell proliferation and reduces apoptosis by repressing the expression of adenylyl cyclase 9 (AC9) in cervical cancer cells.FEBS Lett. 2014 Jan 3;588(1):124-30. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.11.019. Epub 2013 Nov 20. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24269684
-
MiR-125b expression affects the proliferation and apoptosis of human glioma cells by targeting Bmf.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2009;23(4-6):347-58. doi: 10.1159/000218181. Epub 2009 May 6. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19471102
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
MiR-374b-5p suppresses RECK expression and promotes gastric cancer cell invasion and metastasis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Dec 14;20(46):17439-47. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17439. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25516656 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA binding sites in the coding region of mRNAs: extending the repertoire of post-transcriptional gene regulation.Bioessays. 2014 Jun;36(6):617-26. doi: 10.1002/bies.201300104. Epub 2014 Apr 15. Bioessays. 2014. PMID: 24737341 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of TRIB3 mRNA and protein in breast cancer.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49439. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049439. Epub 2012 Nov 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23185332 Free PMC article.
-
emiRIT: a text-mining-based resource for microRNA information.Database (Oxford). 2021 May 28;2021:baab031. doi: 10.1093/database/baab031. Database (Oxford). 2021. PMID: 34048547 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA involvement in human cancer.Carcinogenesis. 2012 Jun;33(6):1126-33. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs140. Epub 2012 Apr 3. Carcinogenesis. 2012. PMID: 22491715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-24 functions as a tumor suppressor in Hep2 laryngeal carcinoma cells partly through down-regulation of the S100A8 protein.Oncol Rep. 2012 Apr;27(4):1097-103. doi: 10.3892/or.2011.1571. Epub 2011 Nov 30. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22139384 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Gemcitabine Sensitivity in Pancreatic Cancer Cells by Restoring miRNA-217 Levels.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 26;11(5):639. doi: 10.3390/biom11050639. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33925948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Axtell MJ. Evolution of microRNAs and their targets: are all microRNAs biologically relevant? Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1779:725–734. - PubMed
-
- Yekta S, Shih IH, Bartel DP. MicroRNA-directed cleavage of HOXB8 mRNA. Science. 2004;304:594–596. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Garcia IM, EA. MicroRNA functions in animal development and human disease. Development. 2005;132:10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

