Holographic photolysis for multiple cell stimulation in mouse hippocampal slices
- PMID: 20195547
- PMCID: PMC2828488
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009431
Holographic photolysis for multiple cell stimulation in mouse hippocampal slices
Abstract
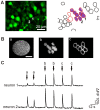
Background: Advanced light microscopy offers sensitive and non-invasive means to image neural activity and to control signaling with photolysable molecules and, recently, light-gated channels. These approaches require precise and yet flexible light excitation patterns. For synchronous stimulation of subsets of cells, they also require large excitation areas with millisecond and micrometric resolution. We have recently developed a new method for such optical control using a phase holographic modulation of optical wave-fronts, which minimizes power loss, enables rapid switching between excitation patterns, and allows a true 3D sculpting of the excitation volumes. In previous studies we have used holographic photololysis to control glutamate uncaging on single neuronal cells. Here, we extend the use of holographic photolysis for the excitation of multiple neurons and of glial cells.
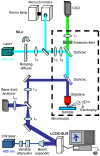
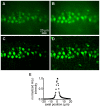
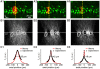
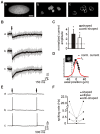
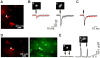
Methods/principal findings: The system combines a liquid crystal device for holographic patterned photostimulation, high-resolution optical imaging, the HiLo microscopy, to define the stimulated regions and a conventional Ca(2+) imaging system to detect neural activity. By means of electrophysiological recordings and calcium imaging in acute hippocampal slices, we show that the use of excitation patterns precisely tailored to the shape of multiple neuronal somata represents a very efficient way for the simultaneous excitation of a group of neurons. In addition, we demonstrate that fast shaped illumination patterns also induce reliable responses in single glial cells.
Conclusions/significance: We show that the main advantage of holographic illumination is that it allows for an efficient excitation of multiple cells with a spatiotemporal resolution unachievable with other existing approaches. Although this paper focuses on the photoactivation of caged molecules, our approach will surely prove very efficient for other probes, such as light-gated channels, genetically encoded photoactivatable proteins, photoactivatable fluorescent proteins, and voltage-sensitive dyes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Holographic photolysis of caged neurotransmitters.Nat Methods. 2008 Sep;5(9):821-7. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1241. Nat Methods. 2008. PMID: 19160517 Free PMC article.
-
A compact holographic projector module for high-resolution 3D multi-site two-photon photostimulation.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 28;14(1):e0210564. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210564. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30689635 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional holographic photostimulation of the dendritic arbor.J Neural Eng. 2011 Aug;8(4):046002. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/8/4/046002. Epub 2011 May 27. J Neural Eng. 2011. PMID: 21623008
-
Holographic imaging and photostimulation of neural activity.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018 Jun;50:211-221. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2018.03.006. Epub 2018 Apr 13. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29660600 Review.
-
Holographic microscope and its biological application.Neurosci Res. 2022 Jun;179:57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2021.10.012. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Neurosci Res. 2022. PMID: 34740727 Review.
Cited by
-
Scanless two-photon excitation of channelrhodopsin-2.Nat Methods. 2010 Oct;7(10):848-54. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1505. Epub 2010 Sep 19. Nat Methods. 2010. PMID: 20852649 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Subpopulations in preBötzinger Complex Play Distinct Roles in Modulating Inspiratory Rhythm and Pattern.J Neurosci. 2024 Jun 19;44(25):e1928232024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1928-23.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38729762 Free PMC article.
-
All-Optical Interrogation of Neural Circuits.J Neurosci. 2015 Oct 14;35(41):13917-26. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2916-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26468193 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional spatiotemporal focusing of holographic patterns.Nat Commun. 2016 Jun 16;7:11928. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11928. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27306044 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in computer-generated holography for targeted neuronal modulation.Neurophotonics. 2022 Oct;9(4):041409. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.9.4.041409. Epub 2022 Jun 16. Neurophotonics. 2022. PMID: 35719844 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fellin T, Pascual O, Gobbo S, Pozzan T, Haydon PG, et al. Neuronal synchrony mediated by astrocytic glutamate through activation of extrasynaptic NMDA receptors. Neuron. 2004;43:729–743. - PubMed
-
- Perea G, Araque A. Astrocytes potentiate transmitter release at single hippocampal synapses. Science. 2007;317:1083–1086. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

