Metal ion determinants of conantokin dimerization as revealed in the X-ray crystallographic structure of the Cd(2+)/Mg (2+)-con-T[K7gamma] complex
- PMID: 20195692
- PMCID: PMC3693470
- DOI: 10.1007/s00775-010-0633-2
Metal ion determinants of conantokin dimerization as revealed in the X-ray crystallographic structure of the Cd(2+)/Mg (2+)-con-T[K7gamma] complex
Abstract
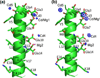
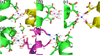
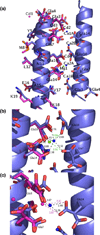
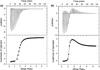
Predatory sea snails from the Conus family produce a variety of venomous small helical peptides called conantokins that are rich in gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) residues. As potent and selective antagonists of the N-methyl-D: -aspartate receptor, these peptides are potential therapeutic agents for a variety of neurological conditions. The two most studied members of this family of peptides are con-G and con-T. Con-G has Gla residues at sequence positions 3, 4, 7, 10, and 14, and requires divalent cation binding to adopt a helical conformation. Although both Ca(2+) and Mg(2+) can fulfill this role, Ca(2+) induces dimerization of con-G, whereas the Mg(2+)-complexed peptide remains monomeric. A variant of con-T, con-T[K7gamma] (gamma is Gla), contains Gla residues at the same five positions as in con-G and behaves very similarly with respect to metal ion binding and dimerization; each peptide binds two Ca(2+) ions and two Mg(2+) ions per helix. To understand the difference in metal ion selectivity, affinity, and the dependence on Ca(2+) for dimer formation, we report here the structure of the monomeric Cd(2+)/Mg(2+)-con-T[K7gamma] complex, and, by comparison with the previously published con-T[K7gamma]/Ca(2+) dimer structure, we suggest explanations for both metal ion binding site specificity and metal-ion-dependent dimerization.
Figures

References
-
- McIntosh J, Olivera BM, Cruz L, Gray W. J Biol Chem. 1984;259:14343–14346. - PubMed
-
- Haack JA, Rivier J, Parks TN, Mena EE, Cruz LJ, Olivera BM. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:6025–6029. - PubMed
-
- Prorok M, Warder SE, Blandl T, Castellino FJ. Biochemistry. 1996;35:16528–16534. - PubMed
-
- Skjaerbaek N, Nielsen KJ, Lewis RJ, Alewood P, Craik DJ. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:2291–2299. - PubMed
-
- Dai Q, Prorok M, Castellino FJ. J Mol Biol. 2004;336:731–744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

