Metabolism of the neuromodulator D-serine
- PMID: 20195697
- PMCID: PMC11115609
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0307-9
Metabolism of the neuromodulator D-serine
Abstract
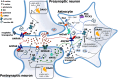
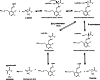
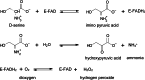
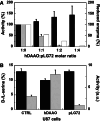
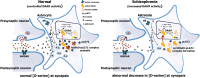
Over the past years, accumulating evidence has indicated that D-serine is the endogenous ligand for the glycine-modulatory binding site on the NR1 subunit of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in various brain areas. D-Serine is synthesized in glial cells and neurons by the pyridoxal-5' phosphate-dependent enzyme serine racemase, and it is released upon activation of glutamate receptors. The cellular concentration of this novel messenger is regulated by both serine racemase isomerization and elimination reactions, as well as by its selective degradation catalyzed by the flavin adenine dinucleotide-containing flavoenzyme D-amino acid oxidase. Here, we present an overview of the current knowledge of the metabolism of D-serine in human brain at the molecular and cellular levels, with a specific emphasis on the brain localization and regulatory pathways of D-serine, serine racemase, and D-amino acid oxidase. Furthermore, we discuss how D-serine is involved with specific pathological conditions related to N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors over- or down-regulation.
Figures
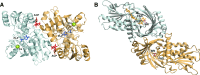
References
-
- Hashimoto A, Oka T, Nishikawa T. Extracellular concentration of endogenous free d-serine in the rat brain as revealed by in vivo microdialysis. Neuroscience. 1995;66:635–643. - PubMed
-
- Danysz W, Parsons CG. Glycine and N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors: physiological significance and possible therapeutic applications. Pharmacol Rev. 1998;50:597–664. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto A, Nishikawa T, Oka T, Takahashi K. Endogenous d-serine in rat brain: N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-related distribution and aging. J Neurochem. 1993;60:783–786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

