Targeting NADPH oxidase and phospholipases A2 in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 20195796
- PMCID: PMC3086559
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-010-8107-7
Targeting NADPH oxidase and phospholipases A2 in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
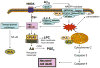
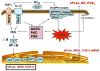
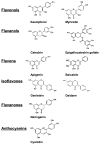
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is marked by an increase in the production of extracellular beta amyloid plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles associated with a decline in brain function. Increases in oxidative stress are regarded as an early sign of AD pathophysiology, although the source of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the mechanism(s) whereby beta amyloid peptides (Abeta) impact oxidative stress have not been adequately investigated. Recent studies provide strong evidence for the involvement of NADPH oxidase and its downstream oxidative signaling pathways in the toxic effects elicited by Abeta. ROS produced by NADPH oxidase activate multiple signaling pathways leading to neuronal excitotoxicity and glial cell-mediated inflammation. This review describes recent studies demonstrating the neurotoxic effects of Abeta in conjunction with ROS produced by NADPH oxidase and the downstream pathways leading to activation of cytosolic phospholipase A(2) (PLA(2)) and secretory PLA(2). In addition, this review also describes recent studies using botanical antioxidants to protect against oxidative damage associated with AD. Investigating the metabolic and signaling pathways involving Abeta NADPH oxidase and PLA(2) can help understand the mechanisms underlying the neurodegenerative effects of oxidative stress in AD. This information should provide new therapeutic approaches for prevention of this debilitating disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Amyloid beta peptide and NMDA induce ROS from NADPH oxidase and AA release from cytosolic phospholipase A2 in cortical neurons.J Neurochem. 2008 Jul;106(1):45-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05347.x. Epub 2008 Jul 1. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 18346200
-
Molecular Roles of NADPH Oxidase-Mediated Oxidative Stress in Alzheimer's Disease: Isoform-Specific Contributions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 15;25(22):12299. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212299. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Aβ-receptor for advanced glycation endproducts interaction in oxidative stress and cytosolic phospholipase A₂ activation in astrocytes and cerebral endothelial cells.Neuroscience. 2011 Dec 29;199:375-85. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.09.038. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21978883 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged exposure of cortical neurons to oligomeric amyloid-β impairs NMDA receptor function via NADPH oxidase-mediated ROS production: protective effect of green tea (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate.ASN Neuro. 2011 Feb 8;3(1):e00050. doi: 10.1042/AN20100025. ASN Neuro. 2011. PMID: 21434871 Free PMC article.
-
NADPH oxidase as a therapeutic target in Alzheimer's disease.BMC Neurosci. 2008 Dec 3;9 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-9-S2-S8. BMC Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19090996 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrating cytosolic phospholipase A₂ with oxidative/nitrosative signaling pathways in neurons: a novel therapeutic strategy for AD.Mol Neurobiol. 2012 Aug;46(1):85-95. doi: 10.1007/s12035-012-8261-1. Epub 2012 Apr 3. Mol Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22476944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Role of Fluoride in the Etiopathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 9;19(12):3965. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123965. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30544885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of the expression and inflammatory activity of NADPH oxidase after spinal cord injury.Free Radic Res. 2014 Aug;48(8):929-39. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2014.927578. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Free Radic Res. 2014. PMID: 24866054 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal Dynamics and Brain Redox Imbalance: Implications in Alzheimer's Disease Pathology and Diagnosis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Mar 5;13(3):316. doi: 10.3390/antiox13030316. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant treatment strategies for hyperphenylalaninemia.Metab Brain Dis. 2013 Dec;28(4):541-50. doi: 10.1007/s11011-013-9414-2. Epub 2013 May 9. Metab Brain Dis. 2013. PMID: 23657560 Review.
References
-
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer’s disease is a synaptic failure. Science. 2002;298:789–791. - PubMed
-
- Butterfield DA. Amyloid beta-peptide [1-42]-associated free radical-induced oxidative stress and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease brain: mechanisms and consequences. Curr Med Chem. 2003;10:2651–2659. - PubMed
-
- Butterfield DA, Castegna A, Lauderback CM, Drake J. Evidence that amyloid beta-peptide-induced lipid peroxidation and its sequelae in Alzheimer’s disease brain contribute to neuronal death. Neurobiol Aging. 2002;23:655–664. - PubMed
-
- Keller JN, Schmitt FA, Scheff SW, Ding Q, Chen Q, Butterfield DA, Markesbery WR. Evidence of increased oxidative damage in subjects with mild cognitive impairment. Neurology. 2005;64:1152–1156. - PubMed
-
- Mattson MP. Oxidative stress, perturbed calcium homeostasis, and immune dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurovirology. 2002;8:539–550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical