A synergistic approach to protein crystallization: combination of a fixed-arm carrier with surface entropy reduction
- PMID: 20196072
- PMCID: PMC2868234
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.368
A synergistic approach to protein crystallization: combination of a fixed-arm carrier with surface entropy reduction
Abstract
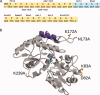
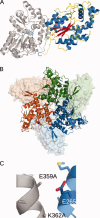
Protein crystallographers are often confronted with recalcitrant proteins not readily crystallizable, or which crystallize in problematic forms. A variety of techniques have been used to surmount such obstacles: crystallization using carrier proteins or antibody complexes, chemical modification, surface entropy reduction, proteolytic digestion, and additive screening. Here we present a synergistic approach for successful crystallization of proteins that do not form diffraction quality crystals using conventional methods. This approach combines favorable aspects of carrier-driven crystallization with surface entropy reduction. We have generated a series of maltose binding protein (MBP) fusion constructs containing different surface mutations designed to reduce surface entropy and encourage crystal lattice formation. The MBP advantageously increases protein expression and solubility, and provides a streamlined purification protocol. Using this technique, we have successfully solved the structures of three unrelated proteins that were previously unattainable. This crystallization technique represents a valuable rescue strategy for protein structure solution when conventional methods fail.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Application of protein engineering to enhance crystallizability and improve crystal properties.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2010 May;66(Pt 5):604-15. doi: 10.1107/S090744491000644X. Epub 2010 Apr 21. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2010. PMID: 20445236 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of MBP fusion proteins.Protein Sci. 2016 Mar;25(3):559-71. doi: 10.1002/pro.2863. Epub 2016 Jan 9. Protein Sci. 2016. PMID: 26682969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MBP-binding DARPins facilitate the crystallization of an MBP fusion protein.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2018 Sep 1;74(Pt 9):549-557. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X18009901. Epub 2018 Aug 29. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2018. PMID: 30198887 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of a signal transduction regulator, RACK1, from Arabidopsis thaliana.Protein Sci. 2008 Oct;17(10):1771-80. doi: 10.1110/ps.035121.108. Epub 2008 Aug 20. Protein Sci. 2008. PMID: 18715992 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of fusion proteins with large-affinity tags.Protein Sci. 2003 Jul;12(7):1313-22. doi: 10.1110/ps.0243403. Protein Sci. 2003. PMID: 12824478 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural Diversity in the Type IV Pili of Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter.J Biol Chem. 2016 Oct 28;291(44):22924-22935. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.751099. Epub 2016 Sep 15. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27634041 Free PMC article.
-
Fusion-protein-assisted protein crystallization.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2015 Jul;71(Pt 7):861-9. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X15011061. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2015. PMID: 26144231 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of human NLRP12 PYD domain and implication in homotypic interaction.PLoS One. 2018 Jan 2;13(1):e0190547. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190547. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29293680 Free PMC article.
-
Protein domain definition should allow for conditional disorder.Protein Sci. 2013 Nov;22(11):1502-18. doi: 10.1002/pro.2336. Epub 2013 Sep 20. Protein Sci. 2013. PMID: 23963781 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into catalytic and substrate binding mechanisms of the strategic EndA nuclease from Streptococcus pneumoniae.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Apr;39(7):2943-53. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1152. Epub 2010 Nov 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21113026 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Means GE, Feeney RE. Reductive alkylation of proteins. Anal Biochem. 1995;224:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Rayment I. Reductive alkylation of lysine residues to alter crystallization properties of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1997;276:171–179. - PubMed
-
- Hegy GB, Shackleton CH, Carlquist M, Bonn T, Engstrom O, Sjoholm P, Witkowska HE. Carboxymethylation of the human estrogen receptor ligand-binding domain-estradiol complex: HPLC/ESMS peptide mapping shows that cysteine 447 does not react with iodoacetic acid. Steroids. 1996;61:367–373. - PubMed
-
- Shiau AK, Barstad D, Loria PM, Cheng L, Kushner PJ, Agard DA, Greene GL. The structural basis of estrogen receptor/coactivator recognition and the antagonism of this interaction by tamoxifen. Cell. 1998;95:927–937. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

