A flexible docking scheme to explore the binding selectivity of PDZ domains
- PMID: 20196074
- PMCID: PMC2868235
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.366
A flexible docking scheme to explore the binding selectivity of PDZ domains
Abstract
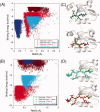
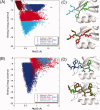
Modeling of protein binding site flexibility in molecular docking is still a challenging problem due to the large conformational space that needs sampling. Here, we propose a flexible receptor docking scheme: A dihedral restrained replica exchange molecular dynamics (REMD), where we incorporate the normal modes obtained by the Elastic Network Model (ENM) as dihedral restraints to speed up the search towards correct binding site conformations. To our knowledge, this is the first approach that uses ENM modes to bias REMD simulations towards binding induced fluctuations in docking studies. In our docking scheme, we first obtain the deformed structures of the unbound protein as initial conformations by moving along the binding fluctuation mode, and perform REMD using the ENM modes as dihedral restraints. Then, we generate an ensemble of multiple receptor conformations (MRCs) by clustering the lowest replica trajectory. Using ROSETTALIGAND, we dock ligands to the clustered conformations to predict the binding pose and affinity. We apply this method to postsynaptic density-95/Dlg/ZO-1 (PDZ) domains; whose dynamics govern their binding specificity. Our approach produces the lowest energy bound complexes with an average ligand root mean square deviation of 0.36 A. We further test our method on (i) homologs and (ii) mutant structures of PDZ where mutations alter the binding selectivity. In both cases, our approach succeeds to predict the correct pose and the affinity of binding peptides. Overall, with this approach, we generate an ensemble of MRCs that leads to predict the binding poses and specificities of a protein complex accurately.
Figures

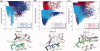
Similar articles
-
The role of flexibility and conformational selection in the binding promiscuity of PDZ domains.PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8(11):e1002749. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002749. Epub 2012 Nov 1. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012. PMID: 23133356 Free PMC article.
-
BP-Dock: a flexible docking scheme for exploring protein-ligand interactions based on unbound structures.J Chem Inf Model. 2014 Mar 24;54(3):913-25. doi: 10.1021/ci4004927. Epub 2014 Mar 4. J Chem Inf Model. 2014. PMID: 24380381 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Docking of Macrocycles in Bound and Unbound Protein Structures with DynaDock.J Chem Inf Model. 2022 Jul 25;62(14):3426-3441. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.2c00436. Epub 2022 Jul 7. J Chem Inf Model. 2022. PMID: 35796228
-
Modeling Binding with Large Conformational Changes: Key Points in Ensemble-Docking Approaches.J Chem Inf Model. 2017 Jul 24;57(7):1563-1578. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.7b00125. Epub 2017 Jun 30. J Chem Inf Model. 2017. PMID: 28616990
-
Pre-existing soft modes of motion uniquely defined by native contact topology facilitate ligand binding to proteins.Protein Sci. 2011 Oct;20(10):1645-58. doi: 10.1002/pro.711. Epub 2011 Sep 9. Protein Sci. 2011. PMID: 21826755 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiscale Gaussian network model (mGNM) and multiscale anisotropic network model (mANM).J Chem Phys. 2015 Nov 28;143(20):204106. doi: 10.1063/1.4936132. J Chem Phys. 2015. PMID: 26627949 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction prediction and classification of PDZ domains.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Jun 30;11:357. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-357. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20591147 Free PMC article.
-
Ancient thioredoxins evolved to modern-day stability-function requirement by altering native state ensemble.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Jun 19;373(1749):20170184. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2017.0184. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29735738 Free PMC article.
-
The role of flexibility and conformational selection in the binding promiscuity of PDZ domains.PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8(11):e1002749. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002749. Epub 2012 Nov 1. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012. PMID: 23133356 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple-targeting and conformational selection in the estrogen receptor: computation and experiment.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2011 Jul;78(1):137-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2011.01119.x. Epub 2011 Apr 27. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2011. PMID: 21443691 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Halperin I, Ma B, Wolfson H, Nussinov R. Principles of docking: an overview of search algorithms and a guide to scoring functions. Proteins: Struct Funct Bioinf. 2002;47:409–443. - PubMed
-
- Leach AR. Molecular Modelling: Principles and Applications. New York: Prentice Hall; 2001.
-
- Mohan V, Gibbs AC, Cummings MD, Jaeger EP, DesJarlais RL. Docking: successes and challenges. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11:323–333. - PubMed
-
- Sousa SF, Fernandes PA, Ramos MJ. Protein-ligand docking: current status and future challenges. Proteins: Struct Funct Bioinf. 2006;65:15–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

