Mechanism of C-F reductive elimination from palladium(IV) fluorides
- PMID: 20196595
- PMCID: PMC2852535
- DOI: 10.1021/ja909371t
Mechanism of C-F reductive elimination from palladium(IV) fluorides
Erratum in
- J Am Chem Soc. 2010 Apr 28;132(16):5922
Abstract
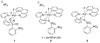
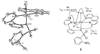
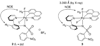
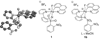
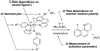
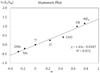
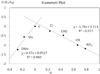
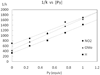
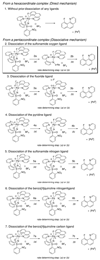
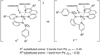
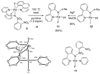
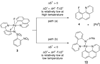
The first systematic mechanism study of C-F reductive elimination from a transition metal complex is described. C-F bond formation from three different Pd(IV) fluoride complexes was mechanistically evaluated. The experimental data suggest that reductive elimination occurs from cationic Pd(IV) fluoride complexes via a dissociative mechanism. The ancillary pyridyl-sulfonamide ligand plays a crucial role for C-F reductive elimination, likely due to a kappa(3) coordination mode, in which an oxygen atom of the sulfonyl group coordinates to Pd. The pyridyl-sulfonamide can support Pd(IV) and has the appropriate geometry and electronic structure to induce reductive elimination.
Figures












References
-
- Jeschke P. Chembiochem. 2004;5:570–589. - PubMed
-
- Phelps ME. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2000;97:9226–9233. - PMC - PubMed
- Lasne MC, Perrio C, Rouden J, Barre L, Roeda D, Dolle F, Crouzel C. Contrast Agents II. Vol. 222. Berlin: Springer; 2002. Chemistry of beta(+)-emitting compounds based on fluorine-18; pp. 201–258.
- Ametamey SM, Honer M, Schubiger PA. Chem. Rev. 2008;108:1501–1516. - PubMed
-
- Sandford G. J. Fluorine Chem. 2007;128:90–104.
-
- Adams DJ, Clark JH. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1999;28:225–231.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

