Toll-like receptor stimulation differentially regulates vasoactive intestinal peptide type 2 receptor in macrophages
- PMID: 20196778
- PMCID: PMC4516478
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00662.x
Toll-like receptor stimulation differentially regulates vasoactive intestinal peptide type 2 receptor in macrophages
Abstract
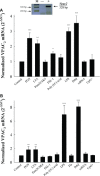
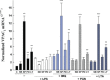
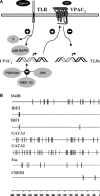
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) was originally isolated as a vasodilator intestinal peptide, then as a neuropeptide. In the immune system, VIP is described as an endogenous macrophage-deactivating factor. VIP exerts its immunological actions in a paracrine and/or autocrine manner, through specific receptors. However, very little is known about the molecular regulation of VIP type 2 receptor (VPAC(2)) in the immune system. We now report that different toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands selectively regulate the VPAC(2) receptor gene and show a gene repression system controlled by key protein kinase signalling cascades in macrophages. VPAC(2) gene expression is regulated by gram-positive (TLR2 ligands) and gram-negative bacteria wall constituents (TLR4 ligands). Moreover, VPAC(2) is tightly regulated: TLR2- or TLR2/6- but not TLR2/1-mediated mechanisms are responsible for the induction of VPAC(2). TLR stimulation by viral or bacterial nucleic acids did not modify the VPAC(2) mRNA levels. Remarkably, imiquimod--a synthetic TLR7 ligand--led to a potent up-regulation of VPAC(2) gene expression. TLR5 stimulation by flagellin present in gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria did not affect VPAC(2) mRNA. The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activity accounted for the TLR4-mediated induction of VPAC(2) gene expression. Surprisingly, our data strongly suggest for the first time a tightly repressed control of VPAC(2) mRNA induction by elements downstream of MAPK kinase 1/2, PI3K/Akt, and particularly Jun-NH(2)-terminal kinase signalling pathways.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ligand-induced differential cross-regulation of Toll-like receptors 2, 4 and 5 in intestinal epithelial cells.Mol Immunol. 2007 Jul;44(15):3702-14. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.04.001. Epub 2007 May 9. Mol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17493681
-
Stimulatory and suppressive signal transduction regulates vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor-1 (VPAC-1) in primary mouse CD4 T cells.Brain Behav Immun. 2008 Oct;22(7):1024-1031. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2008.04.006. Epub 2008 Jun 13. Brain Behav Immun. 2008. PMID: 18555660 Free PMC article.
-
Different vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptor domains are involved in the selective recognition of two VPAC(2)-selective ligands.Mol Pharmacol. 1999 Dec;56(6):1280-7. doi: 10.1124/mol.56.6.1280. Mol Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10570056
-
VPAC and PAC receptors: From ligands to function.Pharmacol Ther. 2009 Mar;121(3):294-316. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2008.11.006. Epub 2008 Dec 6. Pharmacol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19109992 Review.
-
[Physiological significance of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) in the nervous system].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2002 Dec;122(12):1109-21. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.122.1109. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2002. PMID: 12510388 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Monocytes from Sjögren's syndrome patients display increased vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor 2 expression and impaired apoptotic cell phagocytosis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2014 Sep;177(3):662-70. doi: 10.1111/cei.12378. Clin Exp Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24827637 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging neuropeptide targets in inflammation: NPY and VIP.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013 Jun 1;304(11):G949-57. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00493.2012. Epub 2013 Mar 28. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23538492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VPAC1 overexpression is associated with poor differentiation in colon cancer.Tumour Biol. 2014 Jul;35(7):6397-404. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-1852-x. Epub 2014 Mar 28. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24671823
-
The Enteric Network: Interactions between the Immune and Nervous Systems of the Gut.Immunity. 2017 Jun 20;46(6):910-926. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.05.011. Immunity. 2017. PMID: 28636959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll Like Receptors Signaling Pathways as a Target for Therapeutic Interventions.Curr Signal Transduct Ther. 2011;6(3):428-440. doi: 10.2174/157436211797483930. Curr Signal Transduct Ther. 2011. PMID: 28373830 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gonzalez-Rey E, Chorny A, Delgado M. Regulation of immune tolerance by anti-inflammatory neuropeptides. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:52–63. - PubMed
-
- Pozo D, Delgado M. The many faces of VIP in neuroimmunology: a cytokine rather a neuropeptide. FASEB J. 2004;18:1325–34. - PubMed
-
- Martinez C, Delgado M, Abad C, et al. Regulation of VIP production and secretion by murine lymphocytes. J Neuroimmunol. 1999;93:126–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

