Agonist-selective dynamic compartmentalization of human Mu opioid receptor as revealed by resolutive FRAP analysis
- PMID: 20197280
- PMCID: PMC2863218
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.076695
Agonist-selective dynamic compartmentalization of human Mu opioid receptor as revealed by resolutive FRAP analysis
Erratum in
- J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 25;285(26):20422. Saulière-Nzeh, Aude Ndong [corrected to Saulière-Nzeh Ndong, Aude]
Abstract
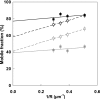
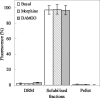
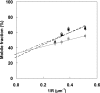
Techniques for analyzing the membrane diffusion of molecules are the most promising methods for investigating the compartmentalization of G-protein-coupled receptors, particularly as relevant to receptor signaling processes. Here, we report fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) measurements performed at variable spot radius for human mu opioid (hMOP) receptors on SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells in the presence of ligands. Although an antagonist did not affect the behavior of the receptors compared with the basal state, two different agonists, DAMGO and morphine, caused markedly different changes to receptor diffusion. Like receptors in the absence of ligand, receptors bound to morphine exhibited diffusion confined to joined semipermeable domains, but with smaller domain size and diffusion coefficient. This effect was inhibited by pertussis toxin, strongly suggesting that this dynamic behavior is associated with early steps of signaling. In the presence of DAMGO, half of the receptors displayed free long-range diffusion and the other half were confined to smaller isolated domains. Hypertonic sucrose buffer suppressed this effect, which we attribute to receptor entry into clathrin-coated pits. It is likely that the observation of distinct receptor dynamics in the presence of DAMGO and morphine involves the agonist-selective phosphorylation of the receptor.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Biased μ-opioid receptor agonists diversely regulate lateral mobility and functional coupling of the receptor to its cognate G proteins.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016 Dec;389(12):1289-1300. doi: 10.1007/s00210-016-1293-8. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27600870
-
Internalization and recycling of human mu opioid receptors expressed in Sf9 insect cells.Life Sci. 2003 May 23;73(1):115-28. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(03)00250-9. Life Sci. 2003. PMID: 12726892
-
delta- and mu-opioid receptor mobilization of intracellular calcium in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Jan;117(2):333-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15195.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8789387 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct differences between morphine- and [D-Ala2,N-MePhe4,Gly-ol5]-enkephalin-mu-opioid receptor complexes demonstrated by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation.J Neurochem. 1998 Jul;71(1):231-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.71010231.x. J Neurochem. 1998. PMID: 9648870
-
Role of protein kinase C (PKC) in agonist-induced mu-opioid receptor down-regulation: I. PKC translocation to the membrane of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells is induced by mu-opioid agonists.J Neurochem. 1999 Feb;72(2):585-93. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0720585.x. J Neurochem. 1999. PMID: 9930730
Cited by
-
Making structural sense of dimerization interfaces of delta opioid receptor homodimers.Biochemistry. 2011 Mar 15;50(10):1682-90. doi: 10.1021/bi101474v. Epub 2011 Feb 9. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21261298 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-directed signalling within the opioid receptor family.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Nov;167(5):960-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02075.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22708627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterologous regulation of Mu-opioid (MOP) receptor mobility in the membrane of SH-SY5Y cells.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 10;289(41):28697-706. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.588558. Epub 2014 Sep 2. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25183007 Free PMC article.
-
Probing Native CB2 Receptor Mobility in Plasma Membranes of Living Cells by Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching.Chembiochem. 2025 Apr 14;26(8):e202400921. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202400921. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Chembiochem. 2025. PMID: 39817417 Free PMC article.
-
GRK Mediates μ-Opioid Receptor Plasma Membrane Reorganization.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 May 1;12:104. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00104. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31118885 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

