Effect of oncostatin M on uridine diphosphate-5'-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 through cross talk with constitutive androstane receptor
- PMID: 20197307
- PMCID: PMC2852350
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0478
Effect of oncostatin M on uridine diphosphate-5'-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 through cross talk with constitutive androstane receptor
Abstract
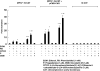
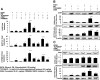
Hyperbilirubinemia remains a common condition in neonates. The constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) is an orphan nuclear receptor that has been shown to participate in the activation of the uridine diphosphate-5'-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 (UGT1A1) gene, which plays an important role in bilirubin clearance. Oncostatin M (OSM), a member of the IL-6 family, is involved in the maturation of fetal hepatocytes. We have demonstrated that low OSM levels are a potential indicator of neonatal jaundice and the need for phototherapy. In this study we examined the effects of OSM on CAR-mediated signaling to investigate its potential role in neonatal jaundice via the CAR-UGT1A1 pathway. We observed that OSM positively augmented the CAR and UGT1A1 expressions and CAR-mediated signaling in vivo and in vitro, through cross talk between the nuclear CAR receptor and the plasma membrane OSM receptor, via the MAPK cascade. These data suggest that OSM might play a role in bilirubin metabolism via the CAR-UGT1A1 pathway.
Figures

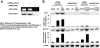

References
-
- Stoll BJ, Kliegman RM 2006 Jaundice and hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn. In: Behrman RE, Kliegman RM, Jenson HB, eds. Nelson textbook of pediatrics, 18th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders; 592–599
-
- Bartoletti AL, Stevenson DK, Ostrander CR, Johnson JD 1979 Pulmonary excretion of carbon monoxide in the human infant as an index of bilirubin production. l. Effects of gestational and postnatal age and some common neonate abnormalities. J Pediatr 94:952–955 - PubMed
-
- Choi HS, Chung M, Tzameli I, Simha D, Lee YK, Seol W, Moore DD 1997 Differential transactivation by two isoforms of the orphan nuclear hormone receptor CAR. J Biol Chem 272:23565–23571 - PubMed

