Spt4/5 stimulates transcription elongation through the RNA polymerase clamp coiled-coil motif
- PMID: 20197319
- PMCID: PMC2896526
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq135
Spt4/5 stimulates transcription elongation through the RNA polymerase clamp coiled-coil motif
Abstract
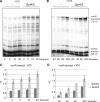
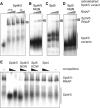
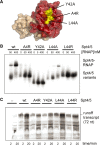
Spt5 is the only known RNA polymerase-associated factor that is conserved in all three domains of life. We have solved the structure of the Methanococcus jannaschii Spt4/5 complex by X-ray crystallography, and characterized its function and interaction with the archaeal RNAP in a wholly recombinant in vitro transcription system. Archaeal Spt4 and Spt5 form a stable complex that associates with RNAP independently of the DNA-RNA scaffold of the elongation complex. The association of Spt4/5 with RNAP results in a stimulation of transcription processivity, both in the absence and the presence of the non-template strand. A domain deletion analysis reveals the molecular anatomy of Spt4/5--the Spt5 Nus-G N-terminal (NGN) domain is the effector domain of the complex that both mediates the interaction with RNAP and is essential for its elongation activity. Using a mutagenesis approach, we have identified a hydrophobic pocket on the Spt5 NGN domain as binding site for RNAP, and reciprocally the RNAP clamp coiled-coil motif as binding site for Spt4/5.
Figures


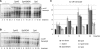

Similar articles
-
The initiation factor TFE and the elongation factor Spt4/5 compete for the RNAP clamp during transcription initiation and elongation.Mol Cell. 2011 Jul 22;43(2):263-74. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.05.030. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21777815 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of archaeal RNA polymerase transcription elongation and Spt4/5 recruitment.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jun 10;52(10):6017-6035. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae282. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38709902 Free PMC article.
-
Architecture of the RNA polymerase-Spt4/5 complex and basis of universal transcription processivity.EMBO J. 2011 Apr 6;30(7):1302-10. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.64. Epub 2011 Mar 8. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21386817 Free PMC article.
-
NusG-Spt5 Transcription Factors: Universal, Dynamic Modulators of Gene Expression.J Mol Biol. 2025 Jan 1;437(1):168814. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168814. Epub 2024 Oct 5. J Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39374889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Spt4-Spt5 complex: a multi-faceted regulator of transcription elongation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1829(1):105-15. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.08.007. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22982195 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pol II waiting in the starting gates: Regulating the transition from transcription initiation into productive elongation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Jan;1809(1):34-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.11.001. Epub 2010 Nov 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21081187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA polymerase I activity is regulated at multiple steps in the transcription cycle: recent insights into factors that influence transcription elongation.Gene. 2012 Feb 10;493(2):176-84. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2011.08.006. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Gene. 2012. PMID: 21893173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spt5 Plays Vital Roles in the Control of Sense and Antisense Transcription Elongation.Mol Cell. 2017 Apr 6;66(1):77-88.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.02.023. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Mol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28366642 Free PMC article.
-
The interplay between nucleoid organization and transcription in archaeal genomes.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015 Jun;13(6):333-41. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3467. Epub 2015 May 6. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25944489 Review.
-
Coupling of Transcription and Translation in Archaea: Cues From the Bacterial World.Front Microbiol. 2021 Apr 29;12:661827. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.661827. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33995325 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Werner F. Structural evolution of multisubunit RNA polymerases. Trends Microbiol. 2008;16:247–250. - PubMed
-
- Landick R. The regulatory roles and mechanism of transcriptional pausing. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006;34:1062–1066. - PubMed
-
- Hartzog GA, Speer JL, Lindstrom DL. Transcript elongation on a nucleoprotein template. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2002;1577:276–286. - PubMed
-
- Hartzog GA. Transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2003;13:119–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

