Skp2 directs Myc-mediated suppression of p27Kip1 yet has modest effects on Myc-driven lymphomagenesis
- PMID: 20197382
- PMCID: PMC3095030
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0232
Skp2 directs Myc-mediated suppression of p27Kip1 yet has modest effects on Myc-driven lymphomagenesis
Abstract
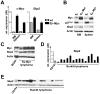
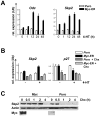
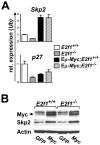
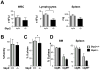
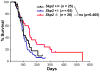
The universal cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(Kip1) functions as a tumor suppressor, and reduced levels of p27(Kip1) connote poor prognosis in several human malignancies. p27(Kip1) levels are predominately regulated by ubiquitin-mediated turnover of the protein, which is marked for destruction by the E3 ubiquitin ligase SCF(Skp2) complex following its phosphorylation by the cyclin E-cyclin-dependent kinase 2 complex. Binding of phospho-p27(Kip1) is directed by the Skp2 F-box protein, and this is greatly augmented by its allosteric regulator Cks1. We have established that programmed expression of c-Myc in the B cells of Emu-Myc transgenic mice triggers p27(Kip1) destruction by inducing Cks1, that this response controls Myc-driven proliferation, and that loss of Cks1 markedly delays Myc-induced lymphomagenesis and cancels the dissemination of these tumors. Here, we report that elevated levels of Skp2 are a characteristic of Emu-Myc lymphomas and of human Burkitt lymphoma that bear MYC/Immunoglobulin chromosomal translocations. As expected, Myc-mediated suppression of p27(Kip1) was abolished in Skp2-null Emu-Myc B cells. However, the effect of Skp2 loss on Myc-driven proliferation and lymphomagenesis was surprisingly modest compared with the effects of Cks1 loss. Collectively, these findings suggest that Cks1 targets, in addition to p27(Kip1), are critical for Myc-driven proliferation and tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors indicate no potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Myc targets Cks1 to provoke the suppression of p27Kip1, proliferation and lymphomagenesis.EMBO J. 2007 May 16;26(10):2562-74. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601691. Epub 2007 Apr 26. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17464290 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant B-RAF signaling and cyclin D1 regulate Cks1/S-phase kinase-associated protein 2-mediated degradation of p27Kip1 in human melanoma cells.Oncogene. 2007 Feb 15;26(7):1056-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209861. Epub 2006 Aug 21. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 16924241
-
EBV latent membrane protein 2A orchestrates p27kip1 degradation via Cks1 to accelerate MYC-driven lymphoma in mice.Blood. 2017 Dec 7;130(23):2516-2526. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-07-796821. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Blood. 2017. PMID: 29074502 Free PMC article.
-
p27(Kip1) signaling: Transcriptional and post-translational regulation.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Nov;68:9-14. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.08.005. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26279144 Review.
-
Loss of cks1 homeostasis deregulates cell division cycle.J Cell Mol Med. 2010 Jan;14(1-2):154-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00698.x. Epub 2009 Feb 17. J Cell Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 19228269 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Skp2 Pathway: A Critical Target for Cancer Therapy.Semin Cancer Biol. 2020 Dec;67(Pt 2):16-33. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.01.013. Epub 2020 Feb 1. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020. PMID: 32014608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional Activation of MYC-Induced Genes by GCN5 Promotes B-cell Lymphomagenesis.Cancer Res. 2020 Dec 15;80(24):5543-5553. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2379. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33168647 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically engineered mouse models for functional studies of SKP1-CUL1-F-box-protein (SCF) E3 ubiquitin ligases.Cell Res. 2013 May;23(5):599-619. doi: 10.1038/cr.2013.44. Epub 2013 Mar 26. Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23528706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cks1 is a critical regulator of hematopoietic stem cell quiescence and cycling, operating upstream of Cdk inhibitors.Oncogene. 2015 Aug 13;34(33):4347-57. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.364. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25417705
-
Characterization of ARF-BP1/HUWE1 interactions with CTCF, MYC, ARF and p53 in MYC-driven B cell neoplasms.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(5):6204-6219. doi: 10.3390/ijms13056204. Epub 2012 May 21. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22754359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sherr CJ, Roberts JM. CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev. 1999;13:1501–12. - PubMed
-
- Coats S, Flanagan WM, Nourse J, Roberts JM. Requirement of p27Kip1 for restriction point control of the fibroblast cell cycle. Science. 1996;272:877–80. - PubMed
-
- Kiyokawa H, Kineman RD, Manova-Todorova KO, et al. Enhanced growth of mice lacking the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor function of p27(Kip1) Cell. 1996;85:721–32. - PubMed
-
- Fero ML, Rivkin M, Tasch M, et al. A syndrome of multiorgan hyperplasia with features of gigantism, tumorigenesis, and female sterility in p27(Kip1)-deficient mice. Cell. 1996;85:733–44. - PubMed
-
- Slingerland J, Pagano M. Regulation of the cdk inhibitor p27 and its deregulation in cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2000;183:10–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

