Complementary actions of inhibitors of angiopoietin-2 and VEGF on tumor angiogenesis and growth
- PMID: 20197469
- PMCID: PMC2840050
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1977
Complementary actions of inhibitors of angiopoietin-2 and VEGF on tumor angiogenesis and growth
Abstract
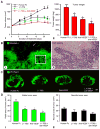
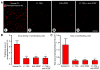
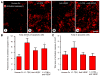
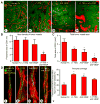
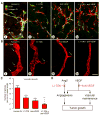
Inhibition of angiopoietin-2 (Ang2) can slow tumor growth, but the underlying mechanism is not fully understood. Because Ang2 is expressed in growing blood vessels and promotes angiogenesis driven by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), we asked whether the antitumor effect of Ang2 inhibition results from reduced sprouting angiogenesis and whether the effect is augmented by inhibition of VEGF from tumor cells. Using Colo205 human colon carcinomas in nude mice as a model, we found that selective inhibition of Ang2 by the peptide-Fc fusion protein L1-7(N) reduced the number of vascular sprouts by 46% and tumor growth by 62% over 26 days. Strikingly, when the Ang2 inhibitor was combined with a function-blocking anti-VEGF antibody, the number of sprouts was reduced by 82%, tumor vascularity was reduced by 67%, and tumor growth slowed by 91% compared with controls. The reduction in tumor growth was accompanied by decreased cell proliferation and increased apoptosis. We conclude that inhibition of Ang2 slows tumor growth by limiting the expansion of the tumor vasculature by sprouting angiogenesis, in a manner that is complemented by concurrent inhibition of VEGF and leads to reduced proliferation and increased apoptosis of tumor cells.
Figures
References
-
- Ferrara N, Kerbel RS. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature. 2005;438:967–74. - PubMed
-
- Tong RT, Boucher Y, Kozin SV, Winkler F, Hicklin DJ, Jain RK. Vascular normalization by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 blockade induces a pressure gradient across the vasculature and improves drug penetration in tumors. Cancer Res. 2004;64:3731–6. - PubMed
-
- Jain RK. Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science. 2005;307:58–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

