Conditional expression of heterozygous or homozygous Jak2V617F from its endogenous promoter induces a polycythemia vera-like disease
- PMID: 20197548
- PMCID: PMC2867267
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-04-215848
Conditional expression of heterozygous or homozygous Jak2V617F from its endogenous promoter induces a polycythemia vera-like disease
Abstract
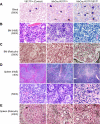
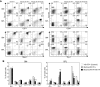
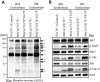
A somatic point mutation (V617F) in the JAK2 tyrosine kinase was found in a majority of patients with polycythemia vera (PV), essential thrombocythemia, and primary myelofibrosis. However, contribution of the JAK2V617F mutation in these 3 clinically distinct myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) remained unclear. To investigate the role of JAK2V617F in the pathogenesis of these MPNs, we generated an inducible Jak2V617F knock-in mouse, in which the expression of Jak2V617F is under control of the endogenous Jak2 promoter. Expression of heterozygous mouse Jak2V617F evoked all major features of human polycythemia vera (PV), which included marked increase in hemoglobin and hematocrit, increased red blood cells, leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, splenomegaly, reduced serum erythropoietin (Epo) levels and Epo-independent erythroid colonies. Homozygous Jak2V617F expression also resulted in a PV-like disease associated with significantly greater reticulocytosis, leukocytosis, neutrophilia and thrombocytosis, marked expansion of erythroid progenitors and Epo-independent erythroid colonies, larger spleen size, and accelerated bone marrow fibrosis compared with heterozygous Jak2V617F expression. Biochemical analyses revealed Jak2V617F gene dosage-dependent activation of Stat5, Akt, and Erk signaling pathways. Our conditional Jak2V617F knock-in mice provide an excellent model that can be used to further understand the molecular pathogenesis of MPNs and to identify additional genetic events that cooperate with Jak2V617F in different MPNs.
Figures



References
-
- James C, Ugo V, Le Couedic JP, et al. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signaling causes polycythemia vera. Nature. 2005;434(7037):1144–1148. - PubMed
-
- Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, et al. Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell. 2005;7(4):387–397. - PubMed
-
- Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, et al. Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet. 2005;365(9464):1054–1061. - PubMed
-
- Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, et al. A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(17):1779–1790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

