Expression of the cytoplasmic NPM1 mutant (NPMc+) causes the expansion of hematopoietic cells in zebrafish
- PMID: 20197555
- PMCID: PMC2858496
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-02-207225
Expression of the cytoplasmic NPM1 mutant (NPMc+) causes the expansion of hematopoietic cells in zebrafish
Abstract
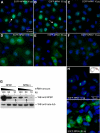
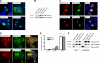
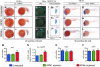
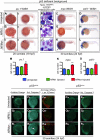
Mutations in the human nucleophosmin (NPM1) gene are the most frequent genetic alteration in adult acute myeloid leukemias (AMLs) and result in aberrant cytoplasmic translocation of this nucleolar phosphoprotein (NPMc+). However, underlying mechanisms leading to leukemogenesis remain unknown. To address this issue, we took advantage of the zebrafish model organism, which expresses 2 genes orthologous to human NPM1, referred to as npm1a and npm1b. Both genes are ubiquitously expressed, and their knockdown produces a reduction in myeloid cell numbers that is specifically rescued by NPM1 expression. In zebrafish, wild-type human NPM1 is nucleolar while NPMc+ is cytoplasmic, as in human AML, and both interact with endogenous zebrafish Npm1a and Npm1b. Forced NPMc+ expression in zebrafish causes an increase in pu.1(+) primitive early myeloid cells. A more marked perturbation of myelopoiesis occurs in p53(m/m) embryos expressing NPMc+, where mpx(+) and csf1r(+) cell numbers are also expanded. Importantly, NPMc+ expression results in increased numbers of definitive hematopoietic cells, including erythromyeloid progenitors in the posterior blood island and c-myb/cd41(+) cells in the ventral wall of the aorta. These results are likely to be relevant to human NPMc+ AML, where the observed NPMc+ multilineage expression pattern implies transformation of a multipotent stem or progenitor cell.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nucleophosmin leukemogenic mutant activates Wnt signaling during zebrafish development.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 23;7(34):55302-55312. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10878. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27486814 Free PMC article.
-
The cytoplasmic NPM mutant induces myeloproliferation in a transgenic mouse model.Blood. 2010 Apr 22;115(16):3341-5. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-208587. Epub 2009 Aug 7. Blood. 2010. PMID: 19666870 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic mutated nucleophosmin is stable in primary leukemic cells and in a xenotransplant model of NPMc+ acute myeloid leukemia in SCID mice.Haematologica. 2008 May;93(5):775-9. doi: 10.3324/haematol.12225. Epub 2008 Mar 26. Haematologica. 2008. PMID: 18367491
-
Nucleophosmin (NPM1) mutations in adult and childhood acute myeloid leukaemia: towards definition of a new leukaemia entity.Hematol Oncol. 2009 Dec;27(4):171-81. doi: 10.1002/hon.904. Hematol Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19569254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered nucleophosmin transport in acute myeloid leukaemia with mutated NPM1: molecular basis and clinical implications.Leukemia. 2009 Oct;23(10):1731-43. doi: 10.1038/leu.2009.124. Epub 2009 Jun 11. Leukemia. 2009. PMID: 19516275 Review.
Cited by
-
Antileukemic activity of nuclear export inhibitors that spare normal hematopoietic cells.Leukemia. 2013 Jan;27(1):66-74. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.219. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Leukemia. 2013. PMID: 22847027 Free PMC article.
-
Myelopoiesis and myeloid leukaemogenesis in the zebrafish.Adv Hematol. 2012;2012:358518. doi: 10.1155/2012/358518. Epub 2012 Jul 19. Adv Hematol. 2012. PMID: 22851971 Free PMC article.
-
Leukemia-Associated Mutations in Nucleophosmin Alter Recognition by CRM1: Molecular Basis of Aberrant Transport.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 19;10(6):e0130610. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130610. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26091065 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in the nucleolar phosphoprotein, nucleophosmin, promote the expression of the oncogenic transcription factor MEF/ELF4 in leukemia cells and potentiates transformation.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 29;288(13):9457-67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.415703. Epub 2013 Feb 7. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23393136 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse models of NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia: biological and clinical implications.Leukemia. 2015 Feb;29(2):269-78. doi: 10.1038/leu.2014.257. Epub 2014 Sep 2. Leukemia. 2015. PMID: 25179729 Review.
References
-
- Grisendi S, Mecucci C, Falini B, Pandolfi PP. Nucleophosmin and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(7):493–505. - PubMed
-
- Colombo E, Marine JC, Danovi D, Falini B, Pelicci PG. Nucleophosmin regulates the stability and transcriptional activity of p53. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4(7):529–533. - PubMed
-
- Wu MH, Yung BY. UV stimulation of nucleophosmin/B23 expression is an immediate-early gene response induced by damaged DNA. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(50):48234–48240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

