Loss of the BMP antagonist USAG-1 ameliorates disease in a mouse model of the progressive hereditary kidney disease Alport syndrome
- PMID: 20197625
- PMCID: PMC2827946
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI39569
Loss of the BMP antagonist USAG-1 ameliorates disease in a mouse model of the progressive hereditary kidney disease Alport syndrome
Abstract
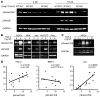
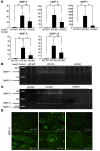
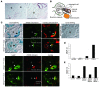
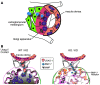
The glomerular basement membrane (GBM) is a key component of the filtering unit in the kidney. Mutations involving any of the collagen IV genes (COL4A3, COL4A4, and COL4A5) affect GBM assembly and cause Alport syndrome, a progressive hereditary kidney disease with no definitive therapy. Previously, we have demonstrated that the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) antagonist uterine sensitization-associated gene-1 (USAG-1) negatively regulates the renoprotective action of BMP-7 in a mouse model of tubular injury during acute renal failure. Here, we investigated the role of USAG-1 in renal function in Col4a3-/- mice, which model Alport syndrome. Ablation of Usag1 in Col4a3-/- mice led to substantial attenuation of disease progression, normalization of GBM ultrastructure, preservation of renal function, and extension of life span. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed that USAG-1 and BMP-7 colocalized in the macula densa in the distal tubules, lying in direct contact with glomerular mesangial cells. Furthermore, in cultured mesangial cells, BMP-7 attenuated and USAG-1 enhanced the expression of MMP-12, a protease that may contribute to GBM degradation. These data suggest that the pathogenetic role of USAG-1 in Col4a3-/- mice might involve crosstalk between kidney tubules and the glomerulus and that inhibition of USAG-1 may be a promising therapeutic approach for the treatment of Alport syndrome.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Upregulated expression of integrin α1 in mesangial cells and integrin α3 and vimentin in podocytes of Col4a3-null (Alport) mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50745. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050745. Epub 2012 Dec 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23236390 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial cell-specific collagen type IV-α3 expression does not rescue Alport syndrome in Col4a3-/- mice.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 May 1;316(5):F830-F837. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00556.2018. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30724107 Free PMC article.
-
A mouse Col4a4 mutation causing Alport glomerulosclerosis with abnormal collagen α3α4α5(IV) trimers.Kidney Int. 2014 Jun;85(6):1461-8. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.493. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Kidney Int. 2014. PMID: 24522496 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a Novel COL4A3 Homozygous/Heterozygous Splicing Mutation on the Mild Phenotype in a Family With Autosomal Recessive Alport Syndrome and a Literature Review.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2025 Feb;13(2):e70053. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.70053. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2025. PMID: 39924725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulator of bone morphogenetic protein activity in the progression of kidney diseases.Kidney Int. 2006 Sep;70(6):989-93. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5001731. Epub 2006 Jul 26. Kidney Int. 2006. PMID: 16871237 Review.
Cited by
-
A review of clinical characteristics and genetic backgrounds in Alport syndrome.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2019 Feb;23(2):158-168. doi: 10.1007/s10157-018-1629-4. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 30128941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BMP signaling and its modifiers in kidney development.Pediatr Nephrol. 2014 Apr;29(4):681-6. doi: 10.1007/s00467-013-2671-9. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Pediatr Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24217785 Review.
-
Modification of an aggressive model of Alport Syndrome reveals early differences in disease pathogenesis due to genetic background.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 31;9(1):20398. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56837-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31892712 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Sostdc1 in skeletal biology and cancer.Front Physiol. 2022 Oct 21;13:1029646. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1029646. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36338475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An update on the pathomechanisms and future therapies of Alport syndrome.Pediatr Nephrol. 2013 Jul;28(7):1025-36. doi: 10.1007/s00467-012-2272-z. Epub 2012 Aug 18. Pediatr Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 22903660 Review.
References
-
- Pescucci C, Longo I, Bruttini M, Mari F, Renieri A. Type-IV collagen related diseases. J Nephrol. 2003;16(2):314–316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

