Interwoven four-compartment capillary membrane technology for three-dimensional perfusion with decentralized mass exchange to scale up embryonic stem cell culture
- PMID: 20197653
- PMCID: PMC2895759
- DOI: 10.1159/000291014
Interwoven four-compartment capillary membrane technology for three-dimensional perfusion with decentralized mass exchange to scale up embryonic stem cell culture
Abstract
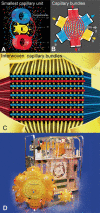
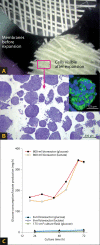
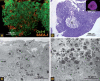
We describe hollow fiber-based three-dimensional (3D) dynamic perfusion bioreactor technology for embryonic stem cells (ESC) which is scalable for laboratory and potentially clinical translation applications. We added 2 more compartments to the typical 2-compartment devices, namely an additional media capillary compartment for countercurrent 'arteriovenous' flow and an oxygenation capillary compartment. Each capillary membrane compartment can be perfused independently. Interweaving the 3 capillary systems to form repetitive units allows bioreactor scalability by multiplying the capillary units and provides decentralized media perfusion while enhancing mass exchange and reducing gradient distances from decimeters to more physiologic lengths of <1 mm. The exterior of the resulting membrane network, the cell compartment, is used as a physically active scaffold for cell aggregation; adjusting intercapillary distances enables control of the size of cell aggregates. To demonstrate the technology, mouse ESC (mESC) were cultured in 8- or 800-ml cell compartment bioreactors. We were able to confirm the hypothesis that this bioreactor enables mESC expansion qualitatively comparable to that obtained with Petri dishes, but on a larger scale. To test this, we compared the growth of 129/SVEV mESC in static two-dimensional Petri dishes with that in 3D perfusion bioreactors. We then tested the feasibility of scaling up the culture. In an 800-ml prototype, we cultured approximately 5 x 10(9) cells, replacing up to 800 conventional 100-mm Petri dishes. Teratoma formation studies in mice confirmed protein expression and gene expression results with regard to maintaining 'stemness' markers during cell expansion.
Copyright 2010 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures


References
-
- Abbott A. Cell culture: biology's new dimension. Nature. 2003;424:870–872. - PubMed
-
- Abranches E., Bekman E., Henrique D., Cabral J.M.S. Expansion of mouse embryonic stem cells on microcarriers. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2007;96:1211–1221. - PubMed
-
- Adewumi O., Aflatoonian B., Ahrlund-Richter L., Amit A., Andrews P.W., Beighton G., Bello P.A., Benvenisty N., Berry L.S., Bevan S., Blum B., Brooking J., Chen K.G., Choo A.B.H., Churchill G.A., Corbel M., Damjanov I., Draper J.S., Dvorak P., Emanuelsson K., Fleck R.A., Ford A., Gertow K., Gertsenstein M., Gokhale P.J., Hamilton R.S., Hampl A., Healy L.E., Hovatta O., Hyllner J., Imreh M.P., Itskovitz-Eldor J., Jackson J., Johnson J.L., Jones M., Kee K., King B.L., Knowles B.B., Lako M., Lebrin F., Mallon B.S., Manning D., Mayshar Y., McKay R.D.G., Michalska A.E., Mikkola M., Mileikovsky M., Minger S.L., Moore H.D., Mummery C.L., Nagy A., Nakatsuji N., O'Brien C.M., Oh S.K.W., Olsson C., Otonkoski T., Park K.Y., Passier R., Patel H., Patel M., Pedersen R., Pera M.F., Piekarczyk M.S., Pera R.A.P., Reubinoff B.E., Robins A.J., Rossant J., Rugg-Gunn P., Schulz T.C., Semb H., Sherrer E.S., Siemen H., Stacey G.N., Stojkovic M., Suemori H., Szatkiewicz J., Turetsky T., Tuuri T., S. van den Brink, K. Vintersten, S. Vuoristo, D. Ward, T.A. Weaver, L.A. Young, W. Zhang. Characterization of human embryonic stem cell lines by the International Stem Cell Initiative. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:803–816. - PubMed
-
- Aleckovic M., C. Simó. Is teratoma formation in stem cell research a characterization tool or a window to developmental biology? Reprod Biomed Online. 2008;17:270–280. - PubMed
-
- Blum B., Benvenisty N. The tumorigenicity of human embryonic stem cells. Adv Cancer Res. 2008;100:133–158. - PubMed

